Divide and Conquer¶
General recurrence: \(T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)\)
Closest Points Problem¶
平面上 N 个点,找到最近的点对。
按照 x 坐标排序,分治地找到左右两边的最近点对,然后找到跨越中线的最近点对。
设左右两边的最近点对距离为 \(d\),设中线为 \(c\),设 \(T_l\) 为左边距离中线小于 \(d\) 的点集,\(T_r\) 为右边距离中线小于 \(d\) 的点集。
设 \(p_l \in S_l, p_r \in S_r\) 满足 \(\mathrm{dist}(p_l, p_r) < d\),则
- \(p_l \in T_l, p_r \in T_r\)
- \(p_l, p_r\) 一定在以中线为对称轴,宽度为 \(2d\) ,高度为 \(d\) 的矩形 \(R\) 内
- \(R\) 内最多有 8 个点,分别在两边 \(d\times d\) 的矩形的四个角上
则将 \(T_l, T_r\) 中的点按照 y 坐标排序为 \((p_n)\),对于每个点 \(p_i\),只需要枚举 \(p_{i+1}, \cdots, p_{i+7}\) 即可。
Time Complexity¶
\(T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)\)
Substitution Method¶
猜测,然后代入证明。
Example
猜测 \(T(n) = O(n\log n)\)。
假设对于 \(m < n\),有 \(T(m) \leq cm\log m\),则 \(T(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor) \leq c\lfloor n/2 \rfloor \log \lfloor n/2 \rfloor\)。
代入得到
所以 \(T(n) = O(n\log n)\)。
Recursion Tree¶
画出递归树,然后求和,然后证明。
Example
递归树如下:
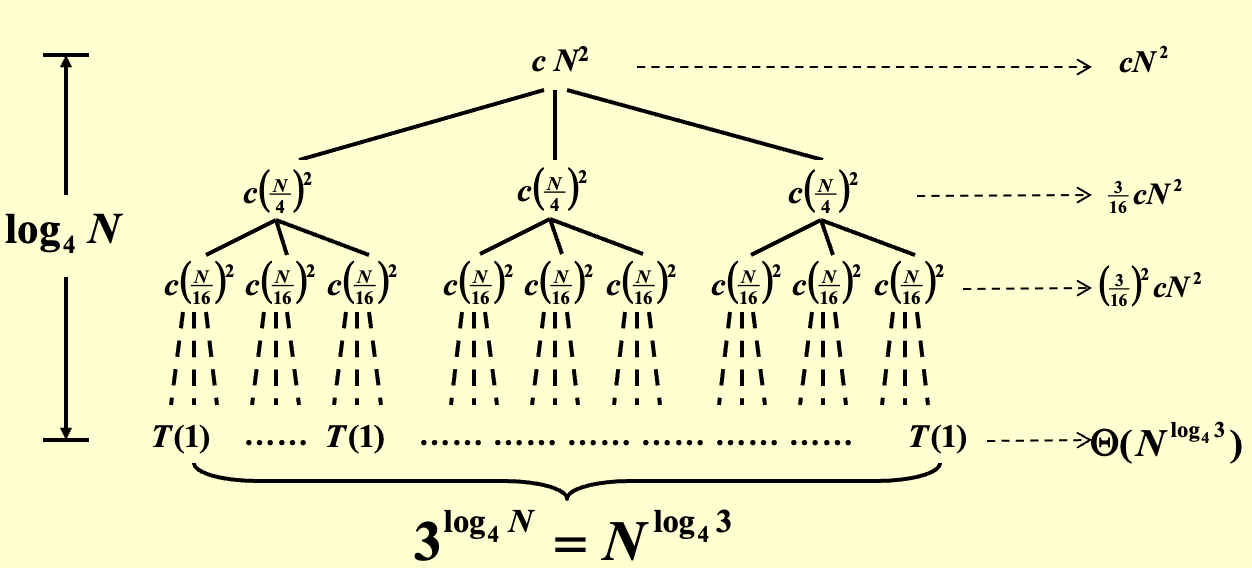
再代入证明
Example
Master Theorem¶
设 \(a \geq 1, b > 1\),\(T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)\)。
- 如果 \(f(n) = O(n^{\log_b a - \epsilon})\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a})\)。
- 如果 \(f(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a})\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a}\log n)\)。
-
如果 \(f(n) = \Omega(n^{\log_b a + \epsilon})\),且对于某个常数 \(c < 1\) 和所有足够大的 \(n\) 有 \(af(n/b) \leq cf(n)\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(f(n))\)。
-
情况 1 表示递归树中叶子节点的开销占据主导,总时间复杂度和叶子个数 \(n^{\log_b a}\) 相关,为 \(O(n^{\log_b a})\)。
- 情况 3 表示递归树中根节点的开销占据主导,总时间复杂度和根节点的开销 \(f(n)\) 相关,为 \(O(f(n))\)。
- 情况 2 表示递归树中根节点和叶子节点的开销相当,总复杂度为 \(O(n^{\log_b a}\log n)\)。
\(\log n\) 渐进小于 \(n^{\epsilon}\)
Another Form¶
Form 1
- 如果 \(af(n/b) = \kappa f(n)\),其中 \(\kappa < 1\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(f(n))\)。(分解任务的开销小于合并任务的开销)
- 如果 \(af(n/b) = K f(n)\),其中 \(K > 1\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a})\)。(分解任务的开销大于合并任务的开销)
- 如果 \(af(n/b) = f(n)\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(f(n)\log_b n)\)。(分解任务和合并任务的开销相当)
Form 2
\(T(n) = aT(n/b) + \Theta(n^k\log^p n)\)。
- 如果 \(a > b^k\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a})\)。
- 如果 \(a = b^k\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^k\log^{p+1} n)\)。
- 如果 \(a < b^k\),则 \(T(n) = \Theta(n^k\log^p n)\)。