Digital Systems and Information¶
Digital Systems 数字系统¶
Discrete Information Processing System 离散信息处理系统
接受离散输入,产生离散输出。
System State 保存状态(内存)
Type of Digital Systems¶
- No state present 没有状态的系统
组合逻辑系统 Combinational Logical System
Output = F(Input)
- State system
分类依据:状态更新时机
-
State update at discrete times
Synchronous Sequential System 同步时序系统
-
State updated at any times
Asyn Sequential System 异步时序系统
状态更新 State = F(State, Input)
输出 Output = F(State) or F(State, Input)
Computer: Syn, 主频:更新状态频率
- Embedded System 嵌入式系统
输入输出通常和物理世界直接相连,如收音、传感器。
模拟信号->数字信号
- 周期采样(香农采样定理:采样频率高于信号最高频率的两倍以上)
- 量化:二进制序列量化(0-5V 内分为 16 份,用二进制表示)
Signal Examples Over Time
- Analog 模拟信号: Continuous in value & time
- Digital 数字信号: Syn 同步、Asyn 异步
Threshold Region 噪声容限:增加传输过程抗干扰能力
Binary Arithmetic¶
-
Addition Carries
-
Subtraction Borrows
-
Multiplication
-
Convert 除以 base 取整
Binary Coding¶
二进制编码
-
非数值编码 Non-numeric 不表示数值(表示颜色、符号等)
-
数值编码 Numeric
- 8,4,-2,-1 Code 每一位有位权。
- Excess 3 Code
每个数字概率相同,1 出现的概率相同
-
BCD 码(8,4,2,1 Code) 每一十进制数位用二进制表示 优点:和人交互更直观
-
BCD Arithmentic 进位:8 + 4 = 13 > 9 13 + 6 -> 1101 + 6 -> 10011 -> 10000 + 3
-
ASCII Code 7 位二进制 '0'->0x30 'A'->0x41 'a'->0x61
Parity Bit Error-Detection Codes¶
检测传输信息正确性 Error Detection.
原理:冗余信息 Redundancy
奇偶校检码,在末尾增加一个二进制位,保证整体 1 的个数奇偶性一致。接收端判断 1 的奇偶。(odd parity and even parity)
Gray Code 格雷码¶
相邻两数之间一位不同。
旋转编码器
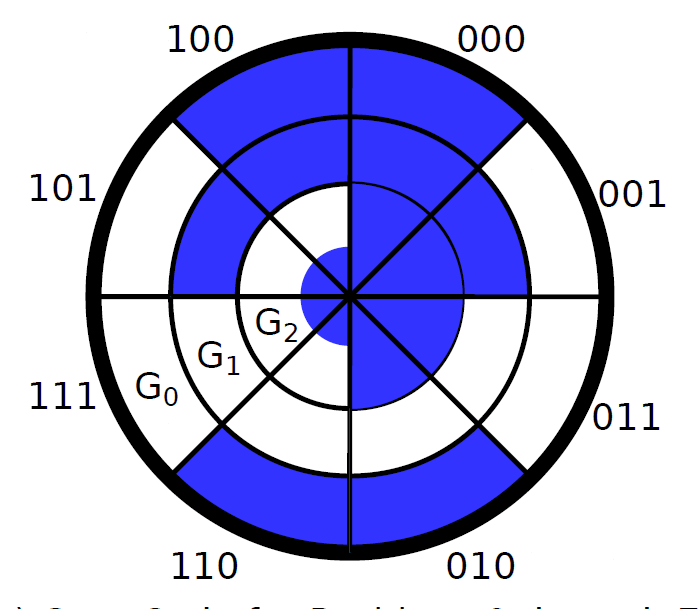
光传感器接收,避免出现中间结果,每次到达下一个状态只会变一位。
UNICODE¶
16-bit (2-byte)