Introduction¶
What is a database?
- Database: A very large, integrated collection of data. 数据集合。
-
Database Management System (DBMS): A software system designed to store, manage, and facilitate access to databases. 数据库管理系统。
DBMS = ( Database ) + A set of programs used to access, update and manage the data in database.
Purpose of Database Systems¶
Database Applications¶
Data processing and management. 主要用于数据处理和管理。
DBMS vs. File-processing Systems¶
-
DBMS:
- Efficiency and scalability in data access. 数据访问效率高,可扩展性强。
- Reduced application development time. 缩短应用开发时间。
- Data independence. 数据独立性。
- Data integrity and security. 数据完整性和安全性。
- Concurrent access and robustness. 并发访问和数据健壮性(可靠性)。
-
File-processing Systems:
- Data redundancy and inconsistency. 数据冗余和不一致。可能存在同一数据的多个副本,且这些副本可能不同步。
- Difficulty in accessing data. 数据访问困难。访问数据需要编写专门的程序。
- Data isolation. 数据隔离。难以检索和共享数据。
- Integrity problems. 完整性问题。难以添加新的约束或者更改已有的约束。
- Atomicity problems. 原子性问题。数据访问失败可能会导致整体数据不同步。
- Concurrent access anomalies. 并发访问异常。
- Security problems. 安全性问题。
View of Data¶
Levels of Data Abstraction¶
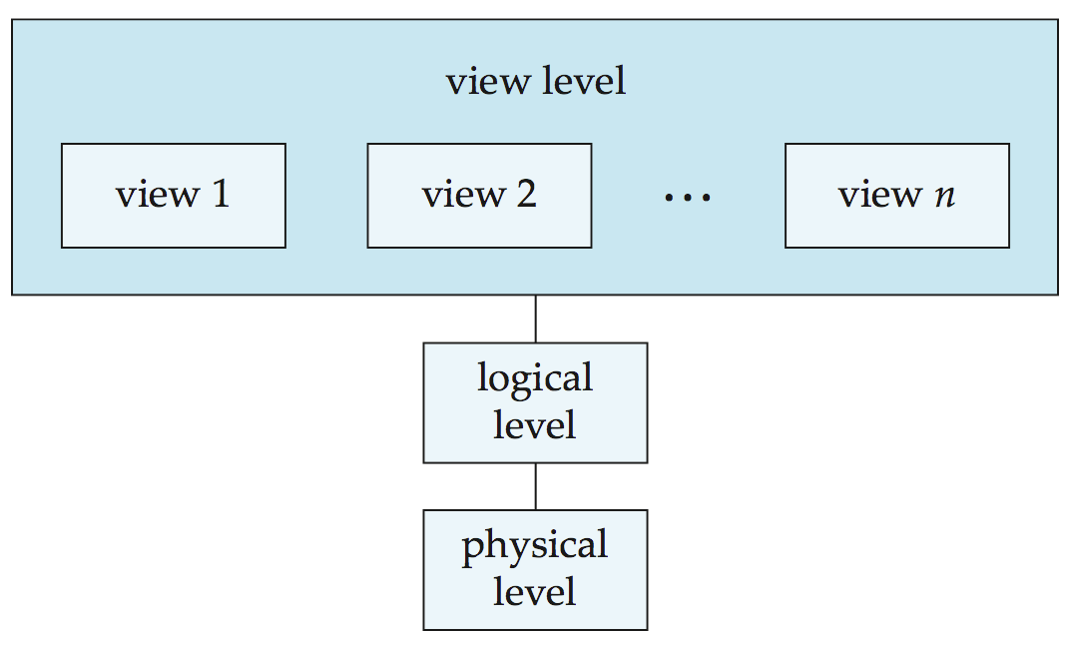
- Physical level: describes how a record is stored. 数据的物理存储方式
- Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data on upper level. 描述数据库中的数据,和数据之间的关系。
- View level: application programs hide details of data types. Note that views can also hide information (e.g., employee’s salary) for security purposes. 选择性向用户展示数据。
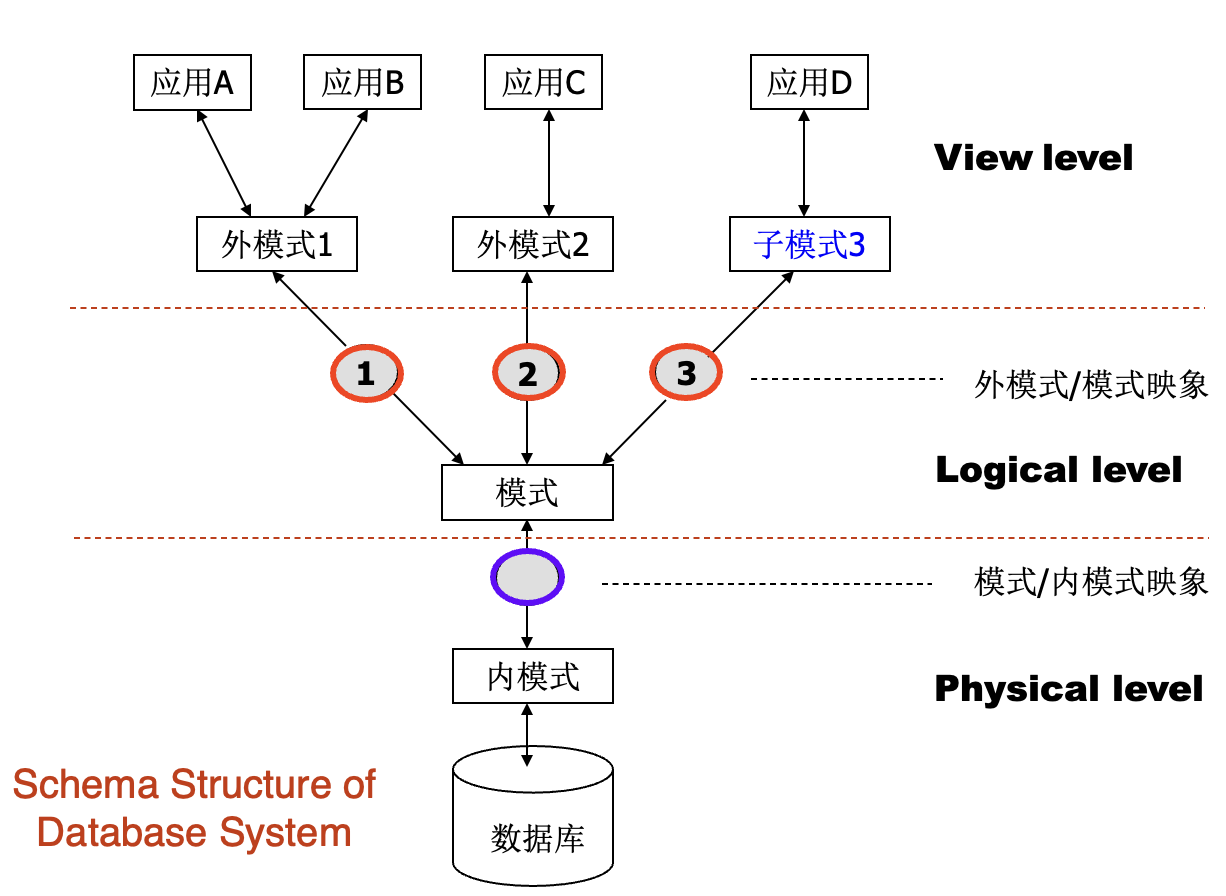
Schemas and Instances¶
-
Schemas 架构: the structure of the database on different levels. 数据库的结构。
- Physical schema: database structure design at the physical level.
- Logical schema: database structure design at the logical level.
- Subschema: schema at view level.
-
Instances 实例: the actual content of the database at a particular point in time. 数据库的实际内容。
类比
- Schema: 类比为数据类型(type)。
- Instance: 类比为实例化后的变量(variable)。
Independence¶
Ability to modify a schema definition at one level without affecting a schema definition at a higher level. 在不影响更高层次的数据的情况下修改底层数据。
- Physical Data Independence: the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema. 可以修改物理架构而不影响逻辑架构。DBMS 的主要优势
- Logical Data Independence: protection from changes in the logical schema. 保护逻辑架构不受应用程序的影响。比较难以实现,因为大部分应用程序都依赖于逻辑架构。
Data Models¶
A collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics, and consistency constraints. 描述数据、数据关系、数据语义和一致性约束的概念工具集合。
- Entity-Relationship model 实体关系模型: 描述实体的属性和实体之间的关系。
- Relational model 关系模型: 描述数据的逻辑结构。
- Others: Object-oriented, Semi-structured data models(XML), etc.
Database design step
- Requirements analysis
- Conceptual design: 使用 ER 模型
- Logical design: 使用关系模型
- ...
Database Language¶
- Data Definition Language (DDL): Specification notation for defining the database schema. 用于定义数据库架构的规范符号。
- Data Manipulation Language (DML): Language for accessing and manipulating the data organized by appropriate data model. 用于访问和操作数据的语言。
- Data Control Language (DCL)
DDL¶
Specify a database schema by a set of definitions expressed by a data-definition language (DDL). The DDL is also used to specify additional properties of the data. DDL 用于定义关系模式、删除关系、修改关系模式以及创建数据库中的各种对象。
DDL 编译后生成一张包含元数据(metadata)的表,称作 data dictionary。
DML¶
用于操纵数据库中的数据,其中涉及数据查询到部分称为查询语言(query language)。
Two classes of DMLs:
- Procedural DMLs 过程式: 用户需要指定如何获取数据。例如 C、Java 等语言。
- Nonprocedural DMLs 非过程式(陈述式): 用户只需要指定需要获取的数据。例如 SQL。
SQL¶
SQL = DDL + DML + DCL
Database Design¶
- Requirement Analysis: What data, applications, and operations needed.
- Conceptual Design: High-level description of data to be stored, using ER model. 高层次描述数据的存储,使用 ER 模型。
- Logical Design: Translate ER model to DB schema. 将 ER 模型转换为数据库架构。
- Schema Refinement: Improve the logical schema. 改进逻辑架构。
- Physical Database Design: Design the internal storage structure. 设计内部存储结构。
- Creating and Initializing the Database: 创建和初始化数据库。
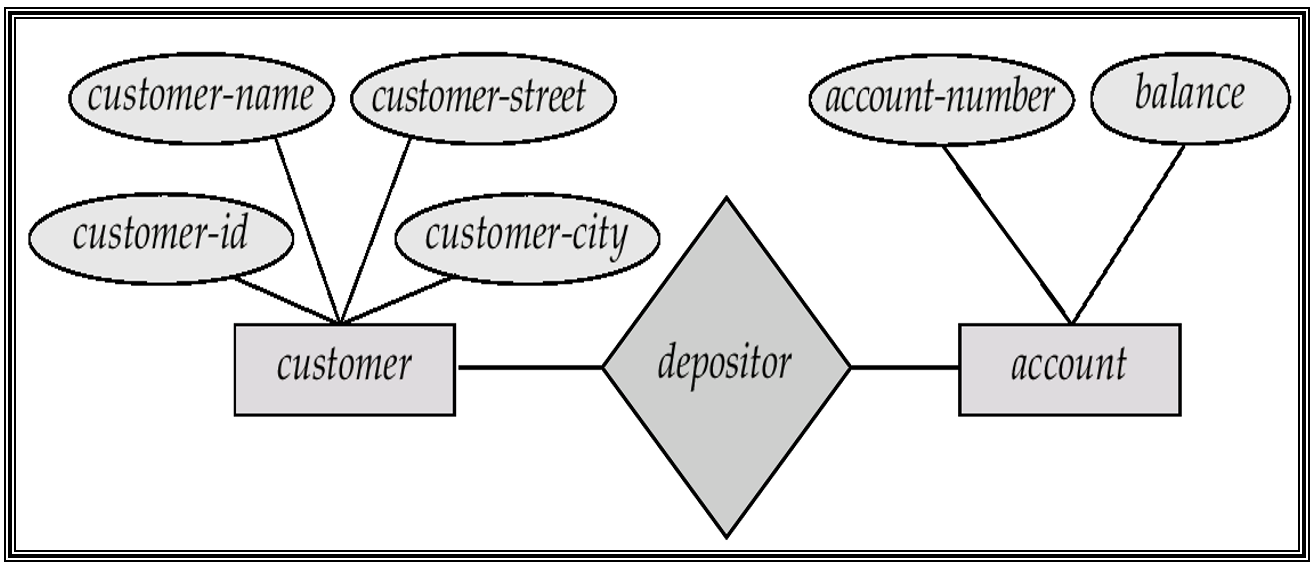
E-R Model¶
ER Model of Real World: - Entities: Entities are described by a set of attributes. 实体由一组属性描述。 - Relationships: Relationships among entities. 实体之间的关系。
Example
Relational Model¶
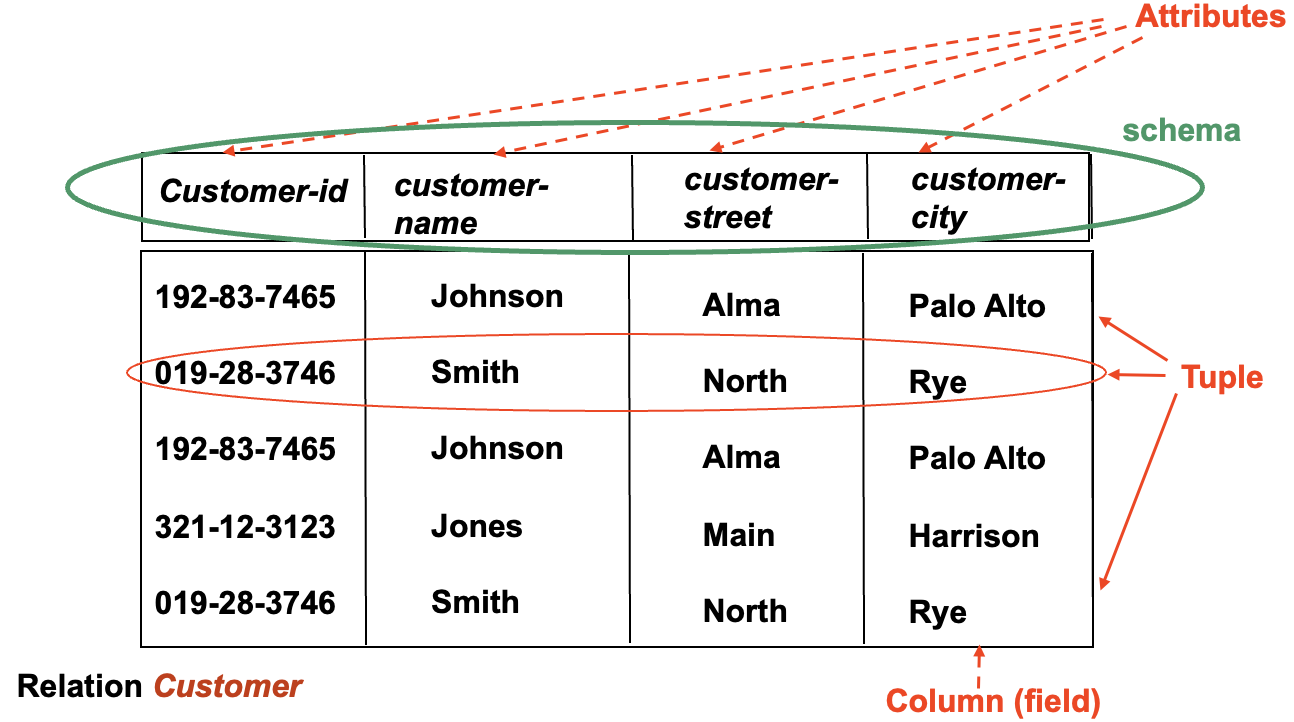
Transfer E-R diagrams into relational schema.
转换后的表格第一行为实体的属性,随后每一行为一个元组,代表一个实例。
Example
将 customer 实体转换为关系模型:
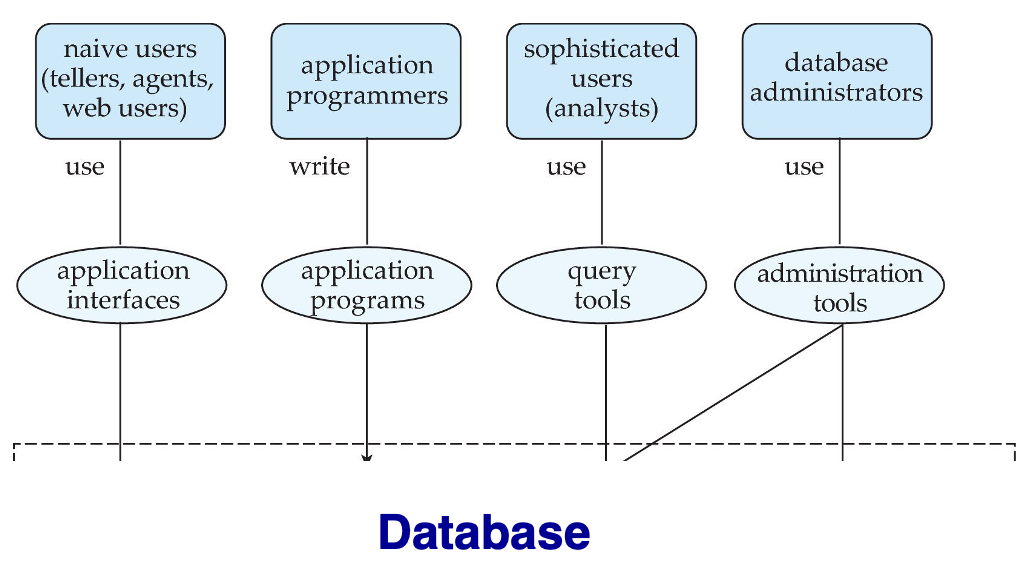
Database Users and Administrators¶
Users¶
由其与系统交互的方式进行划分:
- Naive users: 调用预定义的程序访问数据库,普通用户。
- Application programmers: 开发应用程序的程序员,通过 SQL calls 访问数据库。
- Sophisticated users: 通过 SQL 查询数据库。
- Specialized users: write specialized database applications that do not fit into the traditional data processing framework. 编写专门的数据库应用程序。
Transaction Management¶
A transaction is a collection of operations that performs a single logical function in a database application. 事务是数据库应用程序中执行单个逻辑功能的一组操作。
Transaction requirements include atomicity, consistence, isolation, durability. 事务要求包括原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。
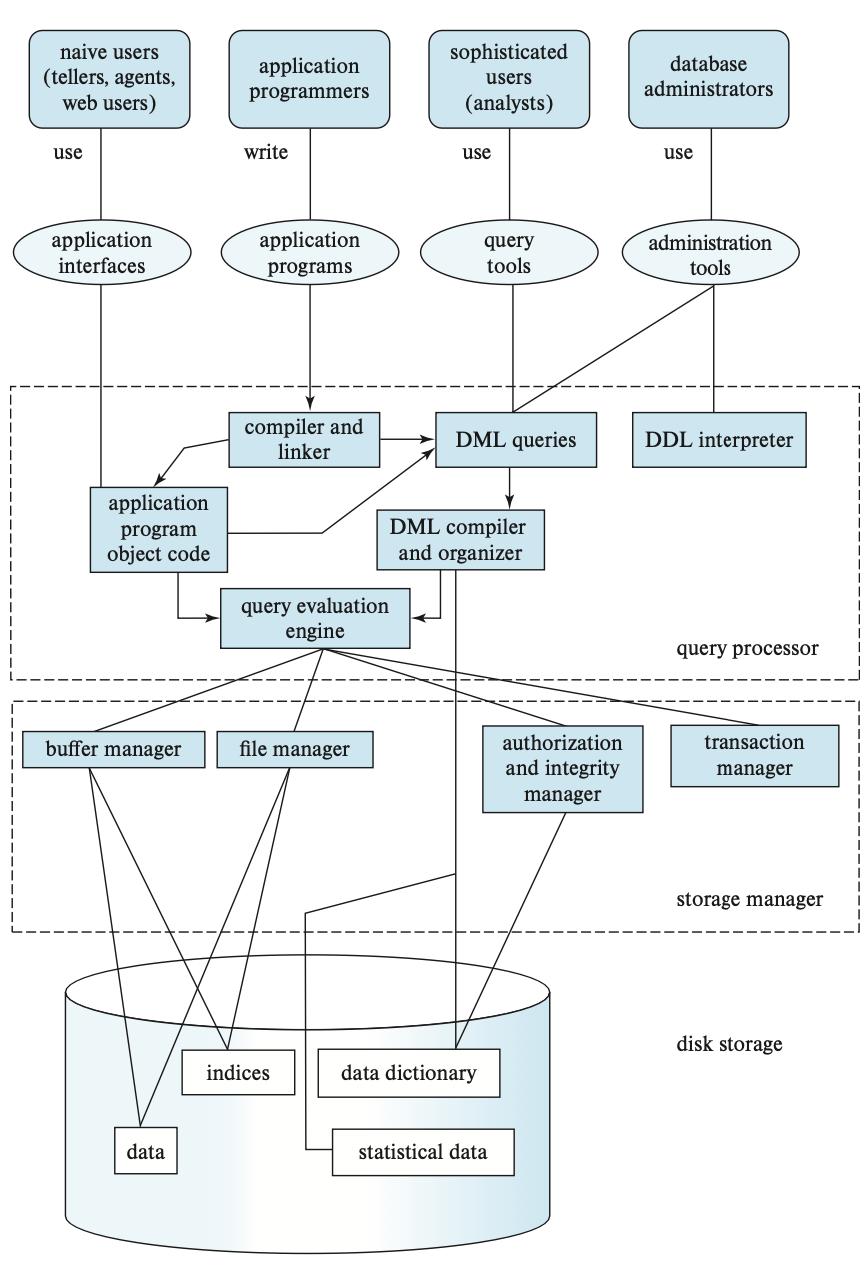
Database Architecture¶
Storage Manager¶
为应用程序提供访问底层数据的接口。分为:
- Transaction manager: 事务管理。
- Authorization and integrity manger: 授权和完整性管理。
- File manager: interaction with the file system to process data files, data dictionary, and index files. 与文件系统交互处理数据文件、数据字典和索引文件。
- Buffer manager: 数据缓存管理。
Query Processor¶
Query Processor includes DDL interpreter, DML compiler, and query processing. 查询处理器包括 DDL 解释器、DML 编译器和查询处理。
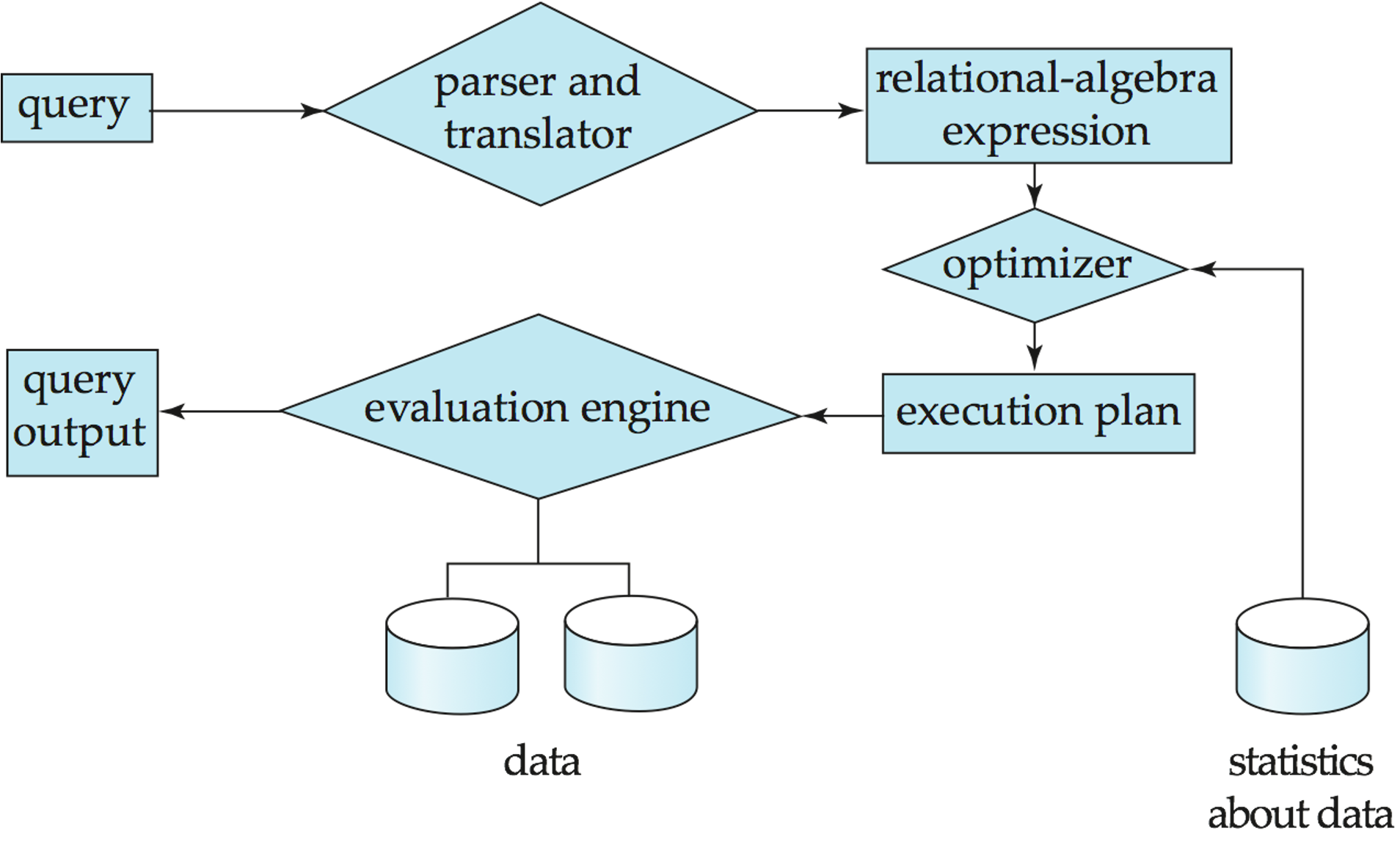
Database System Internals¶