Trees¶
Tree¶
Definition¶
A tree is a collection of nodes. The collection can be empty; otherwise, a tree consists of
- root
- zero or more subtrees, each of whose roots are connected by a directed edge from the root.
树可以为空。如果不为空,树由根节点和若干子树组成,每个子树的根节点通过一条从根出发的有向边与根节点相连。
概念定义:
- degree of a node: the number of its children
- degree of a tree: \(\displaystyle\max_{v \in V} \deg(v)\)
- parent: a node that has subtrees
- child: the roots of subtrees of a parent
- sibling: nodes that have the same parent
- leaf(terminal node): a node that has no children
- path from \(n_1\) to \(n_k\): a sequence of nodes \(n_1, n_2, \dots, n_k\) such that \(n_i\) is the parent of \(n_{i+1}\) for \(i = 1, 2, \dots, k-1\) 从上到下的路径
- path length: the number of edges on the path
- depth of a node: the path length from the root to the node \(n\) 从根到节点的路径长度
- height of a node: the path length from the node \(n\) to the deepest leaf 从节点到最深叶子的路径长度
- height(depth) of a tree: the height of the root 树的高度
- ancestor: all the nodes along the path from the node up to the root 从节点到根的路径上的所有节点
- descendant: all the nodes in the subtree
Implementation¶
List Representation¶
struct TreeNode {
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode LeftChild;
PtrToNode RightChild;
};
First-Child Next-Sibling Representation¶
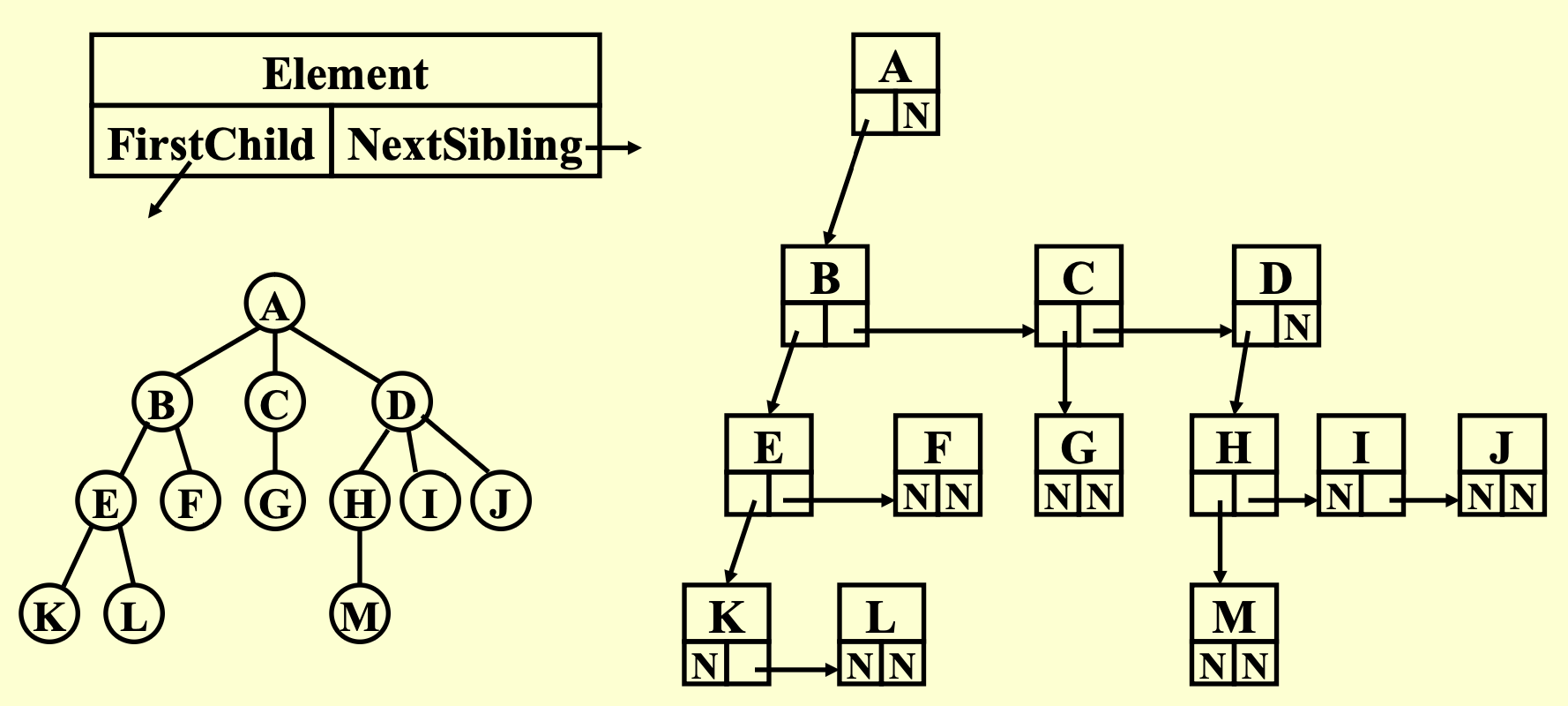
struct TreeNode {
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode FirstChild;
PtrToNode NextSibling;
};
Binary Trees¶
Definition¶
A binary tree is a tree in which no node can have more than two children.
Tree Traversals¶
-
Preorder
void preorder(PtrToNode T) { if (T != NULL) { visit(T); preorder(T->LeftChild); preorder(T->RightChild); } } -
Inorder
void inorder(PtrToNode T) { if (T != NULL) { inorder(T->LeftChild); visit(T); inorder(T->RightChild); } } -
Postorder
void postorder(PtrToNode T) { if (T != NULL) { postorder(T->LeftChild); postorder(T->RightChild); visit(T); } } -
Levelorder
void levelorder(PtrToNode T) { enqueue(T); while (!isEmpty()) { T = dequeue(); visit(T); if (T->LeftChild != NULL) enqueue(T->LeftChild); if (T->RightChild != NULL) enqueue(T->RightChild); } }
Threaded Binary Trees¶
二叉线索树。将遍历顺序保存,方便之后的遍历。
Rules:
-
If a node has no left child, its left pointer points to its inorder predecessor.
如果一个节点没有左儿子,那么它的左指针指向它的中序前驱。
-
If a node has no right child, its right pointer points to its inorder successor.
如果一个节点没有右儿子,那么它的右指针指向它的中序后继。
-
需要增加一个 head node,使得 head->LeftChild 指向根节点,head->RightChild 指向自己。
建立线索二叉树:
void ThreadTree(PtrToNode *p, PtrToNode **pre){
if(p == NULL) return;
ThreadTree(p->LeftChild, pre);
threadNode(p, pre);
ThreadTree(p->RightChild, pre);
}
遍历线索二叉树:
void InorderTraversal(PtrToNode T){
PtrToNode p = T->LeftChild;
while(p != T){
while(p->LeftTag == 0) p = p->LeftChild;
visit(p);
while(p->RightTag == 1 && p->RightChild != T){
p = p->RightChild;
visit(p);
}
p = p->RightChild;
}
}
Properties of Binary Trees¶
形态¶
- full binary tree: every node has either zero or two children 每个节点都有两个子节点或者没有子节点
- complete binary tree: every level except possibly the last is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible 每个节点都有两个子节点,除了最后一层的节点,最后一层的节点尽可能靠左
- perfect binary tree: a full binary tree in which all leaves are at the same level 每个节点都有两个子节点,所有叶子节点都在同一层且填满最后一层
-
skewed binary tree: a binary tree in which all nodes have only one child 每个节点都只有一个子节点
- left skewed: every node has a left child, but no node has a right child 每个节点都有左儿子,但是没有右儿子
- right skewed: every node has a right child, but no node has a left child 每个节点都有右儿子,但是没有左儿子
数量关系¶
- level \(i\) 的节点数最多为 \(2^{i-1}, \quad i \geq 1\)
- depth \(k\) 的二叉树最多有 \(2^k - 1\) 个节点,最少有 \(k\) 个节点
- 设度为 \(\deg\) 的节点总数为 \(n_{\deg}\),则 \(n_0 = n_2 + 1\)
The Search Tree ADT¶
Definition¶
左节点的值小于根节点,右节点的值大于根节点。
Implementation¶
- Find
- Insert
-
Delete
-
case 1: the node to be deleted is a leaf node
直接删除
-
case 2: the node to be deleted has only one child
将子节点提升到被删除节点的位置
-
case 3: the node to be deleted has two children
将右子树的最小节点或者左子树的最大节点提升到被删除节点的位置,然后删除该节点
-
Priority Queues (Heaps)¶
ADT¶
- Operations: Insert, DeleteMin, FindMin, ...
Simple Implementation¶
- Array: \(O(1)\) for Insert, \(O(n)\) for FindMin and then \(O(n)\) for delete
- Linked List: \(O(1)\) for Insert, \(O(n)\) for FindMin and then \(O(1)\) for delete
- Ordered Array: \(O(n)\) for find the position and then \(O(n)\) for insert, \(O(1)\) for DeleteMin or DeleteMax
- Ordered Linked List: \(O(n)\) for find the position and then \(O(1)\) for insert, \(O(1)\) for DeleteMin or DeleteMax
Binary Heap¶
complete binary tree with the heap-order property
使用数组存储,从 1 开始编号,对于节点 \(i\),其父节点为 \(i/2\),左儿子为 \(2i\),右儿子为 \(2i+1\)。
Heap Order Property
A min tree is a tree in which the key value in each node is no larger than the key values in its children (if any). A min heap is a complete binary tree that is also a min tree.
- 最小堆:每个节点的值都小于等于其子节点的值。
- 最大堆:每个节点的值都大于等于其子节点的值。
Operations¶
以最小堆为例。
向上调整和向下调整:
void upAdjust(int p) {
if (p == 1) return;
if (heap[p] < heap[p/2]) {
swap(heap[p], heap[p/2]);
upAdjust(p/2);
}
}
void downAdjust(int p) {
int minIndex = p;
if (p*2 <= size && heap[p*2] < heap[minIndex]) minIndex = p*2;
if (p*2+1 <= size && heap[p*2+1] < heap[minIndex]) minIndex = p*2+1;
if (minIndex != p) {
swap(heap[p], heap[minIndex]);
downAdjust(minIndex);
}
}
- Insert: 放到最后,然后向上调整。
- Deletemin: 将根节点与最后一个节点交换,然后删除最后一个节点,向下调整根节点。
- FindMin: 根节点。
-
BuildHeap: 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,向下调整。复杂度为 \(O(n)\)。
所有节点高度之和
假设树的高度为 \(h\),则高度为 \(i\) 的节点有 \(2^{h-i}\) 个,所有节点高度之和为
\[ \begin{aligned} S(n) &= 2^{h-1} + 2^{h-2} \times 2 + 2^{h-3} \times 3 + \dots + 2^{0} \times h \\ &= O(n - \log_2(n+1)) \\ &= O(n) \end{aligned} \]注意如果向上调整,复杂度为 \(O(n \log n)\)。
d-Heaps¶
每个节点有 \(d\) 个子节点。
向下调整操作需要比较 \(d\) 个节点,所以 DeleteMin 操作复杂度变为 \(O(d \log_d n)\)。
错题整理¶
Question 1
If a binary search tree of N nodes is complete, which one of the following statements is FALSE?
False:
- the maximum key must be at a leaf node.
注意条件。