lab5 简单神经网络训练与加速
实验过程
该部分完整代码位于 ./code/letnet5.py
数据集导入与加载
使用 torchvision.datasets.MNIST 导入数据。
其中使用 torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() 将 PIL image 转换为 Tensor 。
# Load MNIST
train_dataset = torchvision . datasets . MNIST ( './data' ,
train = True ,
transform = torchvision . transforms . ToTensor (),
target_transform = None ,
download = True )
test_dataset = torchvision . datasets . MNIST ( './data' ,
train = False ,
transform = torchvision . transforms . ToTensor (),
target_transform = None ,
download = True )
使用 torch.utils.data.DataLoader 加载数据,batch_size=64 设置一次训练及测试抓取的数据样本数量为 64 ,并且训练时将数据打乱。
# Data Loader
train_loader = torch . utils . data . DataLoader ( train_dataset ,
batch_size = 64 , shuffle = True )
test_loader = torch . utils . data . DataLoader ( test_dataset ,
batch_size = 64 , shuffle = False )
模型编写
网络结构
继承 torch.nn.Module 定义模型,将网络结构以类保存。
根据 LetNet-5 的结构,定义模型中各个层。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class LeNet_5 ( nn . Module ):
def __init__ ( self ):
super ( LeNet_5 , self ) . __init__ ()
# 卷积层
self . conv1 = nn . Conv2d ( 1 , 6 , 5 , stride = 1 )
self . conv2 = nn . Conv2d ( 6 , 16 , 5 , stride = 1 )
# 池化层
self . pool = nn . AvgPool2d ( 2 , stride = 2 )
# 全连接层
self . full1 = nn . Linear ( 16 * 4 * 4 , 120 )
self . full2 = nn . Linear ( 120 , 84 )
self . full3 = nn . Linear ( 84 , 10 )
def forward ( self , x ):
x = F . gelu ( self . conv1 ( x ))
x = F . gelu ( self . pool ( x ))
x = F . gelu ( self . conv2 ( x ))
x = F . gelu ( self . pool ( x ))
x = x . view ( - 1 , 16 * 4 * 4 ) # 得到一维向量
x = F . gelu ( self . full1 ( x ))
x = F . gelu ( self . full2 ( x ))
x = self . full3 ( x )
return x
损失函数及优化器
损失函数使用交叉熵损失函数 torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 。
使用 NAdam 优化器,经多次测试,选用 \(3 \times 10^{-3}\) 的学习率。
criterion = nn . CrossEntropyLoss ()
optimizer = torch . optim . NAdam ( model . parameters (), lr = 3e-3 )
手动迁移模型及数据
定义 device 变量,将模型和数据迁移至 GPU ,若无 GPU 可用,则迁移至 CPU 训练。
device = torch . device ( "cuda" if torch . cuda . is_available () else "cpu" )
model = model . to ( device )
训练过程
总共在训练集上进行十次训练,每次训练时不断从 Dataloader 中取出数据,并且输出每次训练的平均损失。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 model . train ()
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx , ( images , labels ) in enumerate ( train_loader ):
# 取出数据,将数据迁移至 device
images , labels = images . to ( device ), labels . to ( device )
# 对数据进行正向传播
outputs = model ( images )
# 使用损失函数计算该次训练的损失
loss = criterion ( outputs , labels )
# 反向传播前将梯度清零
optimizer . zero_grad ( set_to_none = True )
# 反向传播
loss . backward ()
# 反向传播后更新优化器参数
optimizer . step ()
# 统计损失
running_loss += loss . item ()
# 输出平均损失
print ( 'Epoch: [ {} ], Average Loss: {:.6f} ' . format ( epoch + 1 ,
running_loss / len ( train_loader )))
测试过程
每次训练结束之后,进行一次测试。输出每次训练之后的准确度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 model . eval ()
# 禁用梯度计算
with torch . no_grad ():
corret = 0
total = 0
for batch_idx , ( images , labels ) in enumerate ( test_loader ):
# 取出数据,将数据迁移至 device
images , labels = images . to ( device ), labels . to ( device )
# 对数据进行正向传播
outputs = model ( images )
# 返回每一行最大值及其索引,即预测结果
predict , result = torch . max ( outputs . data , 1 )
# 累加测试数据数量
total += labels . size ( 0 )
# 累加预测正确的数据数量
corret += ( result == labels ) . sum () . item ()
# 输出准确率
print ( 'Test Accuracy: {:.2f} %' . format ( 100 * corret / total ))
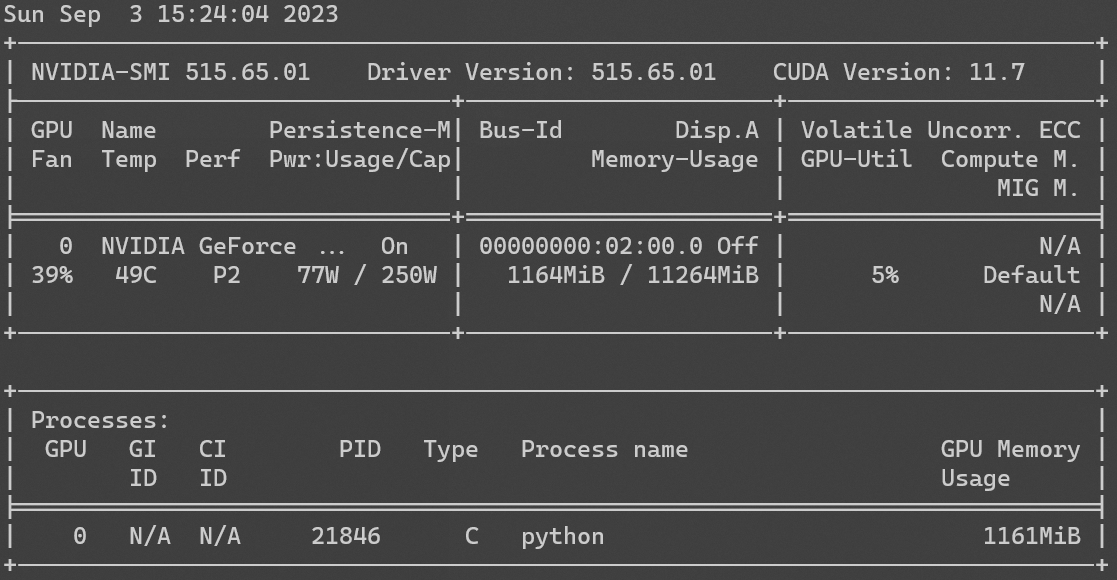
GPU 占用率
使用 nvidia-smi 查看 GPU 占用率如图。
使用 Tensorboard
使用 Tensorboard 记录训练过程中的损失和准确率。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter ()
...
for epoch in range ( 10 ):
...
for batch_idx , ( images , labels ) in enumerate ( train_loader ):
...
writer . add_scalar ( 'Loss/Train' , loss . item (),
epoch * len ( train_loader ) + batch_idx )
writer . flush ()
with torch . no_grad ():
...
for batch_idx , ( images , labels ) in enumerate ( test_loader ):
...
writer . add_scalar ( 'Accuracy/Test' ,
100 * ( result == labels ) . sum () . item () / labels . size ( 0 ),
epoch * len ( test_loader ) + batch_idx )
writer . flush ()
训练结束后,执行
$ tensorboard --logdir= ./path/to/the/folder
其中 ./path/to/the/folder 为 Tensorboard 生成的文件路径。
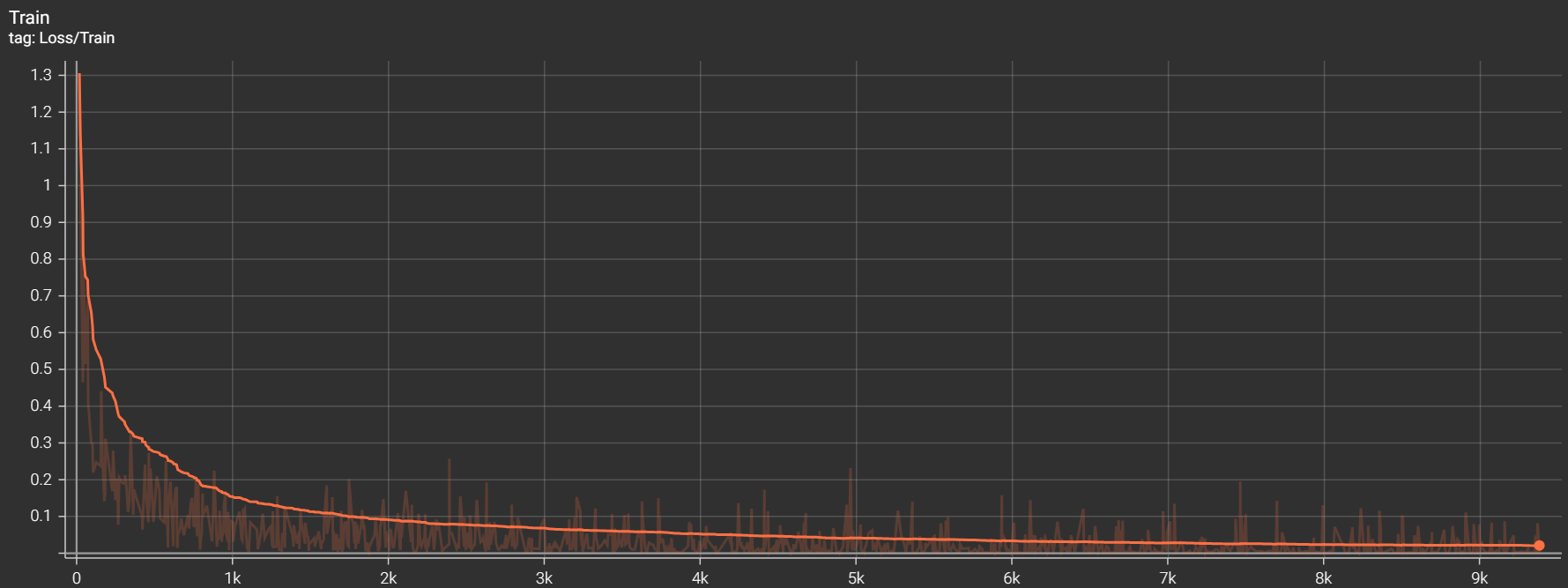
得到损失曲线:
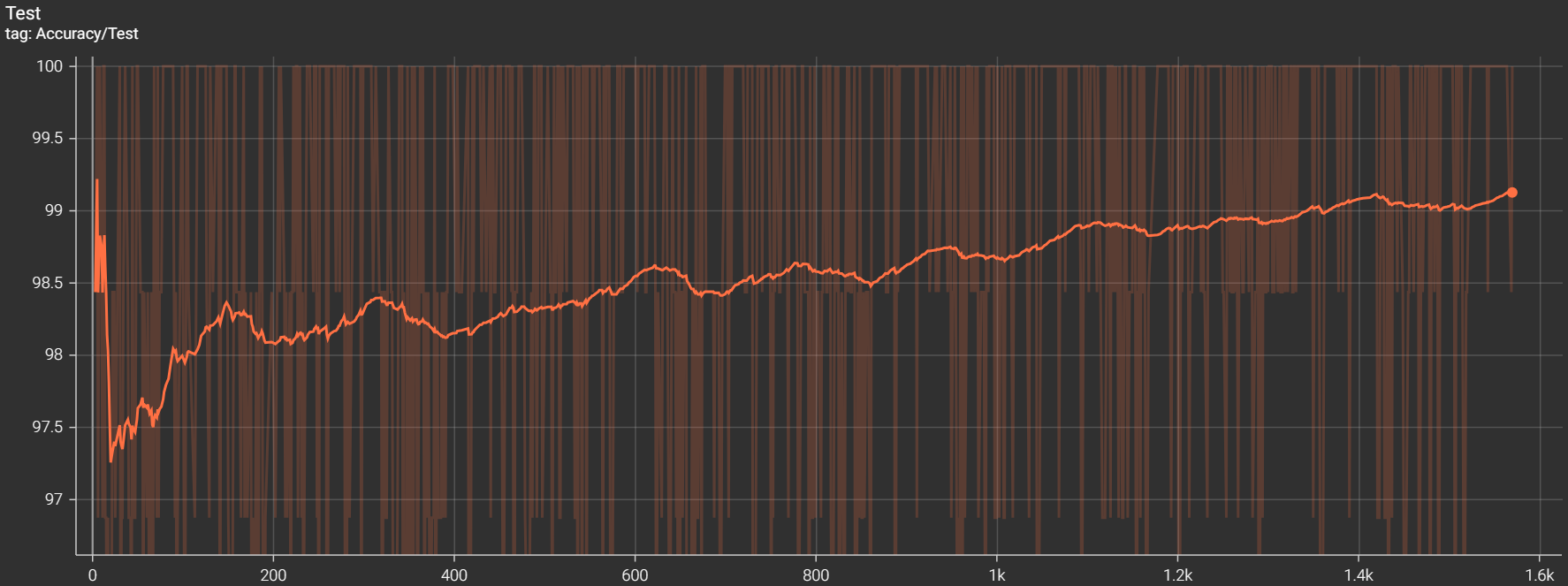
准确率曲线:
最终的识别正确率约为 98.90 % 。
自定义算子
该部分完整代码位于
./code/mygelu.py :自定义 GELU 算子及其验证。./code/mygelu.cpp :C++ 实现 GELU 算子。./code/mygelu_cpp.py :python 调用 C++ GELU 算子验证正确性。./code/letnet5_cpp.py :使用自定义 GELU 算子进行 LetNet-5 训练。
算子编写
GELU 算子公式为:
\[
\begin{align}
\mathrm{GELU}(x) &= x \cdot \Phi(x) \\
&= \frac{1}{2} x (1 + \mathrm{erf}(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}))
\end{align}
\]
求导得:
\[
\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d} x}\mathrm{GELU}(x) = \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{erf}(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}) + \frac{\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} x \mathrm{e}^{-x^2 / 2}}{\sqrt{\pi}}
\]
使用 torch 提供的函数 torch.erf() 实现 GELU 函数及其导数的计算。
继承 torch.autograd.Function 并实现 forward 和 backward 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23 import math
import torch
def GELU ( x ):
return 0.5 * x * ( 1.0 + torch . erf ( x / math . sqrt ( 2 )))
def GELU_gard ( x ):
return 0.5 + 0.5 * torch . erf ( x / math . sqrt ( 2 )) + \
( 0.5 * x * torch . exp ( - x * x / 2 ) * math . sqrt ( 2 )) / math . sqrt ( math . pi )
class my_gelu ( torch . autograd . Function ):
@staticmethod
def forward ( ctx , input ):
# 保存 input 供 backward() 使用
ctx . save_for_backward ( input )
return GELU ( input )
@staticmethod
def backward ( ctx , gard_output ):
input = ctx . saved_tensors
# 计算梯度
gard_input = gard_output * GELU_gard ( input )
return gard_input
将自定义算子与 F.gelu 比较:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 import torch.nn.functional as F
loss_func = nn . MSELoss ()
A = torch . randn ( 100 )
B = A . clone ()
A . requires_grad = True
B . requires_grad = True
c = torch . randn ( 100 )
a = F . gelu ( A )
b = my_gelu . apply ( B )
loss1 = loss_func ( a , c )
loss2 = loss_func ( b , c )
loss1 . backward ()
loss2 . backward ()
gradA = A . grad
gradB = B . grad
err = loss_func ( gradA , gradB )
print ( err . item ())
输出误差约为 \(10^{-17}\) ,可以忽略。
使用 C++
在 C++ 中实现 GELU 算子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 #include <torch/extension.h>
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#include <cmath>
using namespace std ;
torch :: Tensor GELU ( torch :: Tensor x ) {
return 0.5 * x * ( 1.0 + torch :: erf ( x / sqrt ( 2 )));
}
torch :: Tensor GELU_gard ( torch :: Tensor x ) {
return 0.5 + 0.5 * torch :: erf ( x / sqrt ( 2 )) +
( 0.5 * x * torch :: exp ( - x * x / 2 ) * sqrt ( 2 )) / sqrt ( M_PI );
}
torch :: Tensor gelu_forward ( torch :: Tensor input ) {
return GELU ( input );
}
torch :: Tensor gelu_backward ( torch :: Tensor grad_output , torch :: Tensor input ) {
return grad_output * GELU_gard ( input );
}
PYBIND11_MODULE ( TORCH_EXTENSION_NAME , m ) {
m . def ( "forward" , & gelu_forward , "GELU forward" );
m . def ( "backward" , & gelu_backward , "GELU backward" );
}
使用 torch.utils.cpp_extension.load 调用 C++ 共享库,使用 python 调用算子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 from torch.utils.cpp_extension import load
gelu_cpp = load ( name = "gelu_cpp" , sources = [ "mygelu.cpp" ])
class my_gelu ( torch . autograd . Function ):
@staticmethod
def forward ( ctx , input ):
ctx . save_for_backward ( input )
output = gelu_cpp . forward ( input )
return output
@staticmethod
def backward ( ctx , grad_output ):
input , = ctx . saved_tensors
grad_input = gelu_cpp . backward ( grad_output , input )
return grad_input
再次将自定义算子与 F.gelu 比较,误差约为 \(10^{-18}\) ,可以忽略。
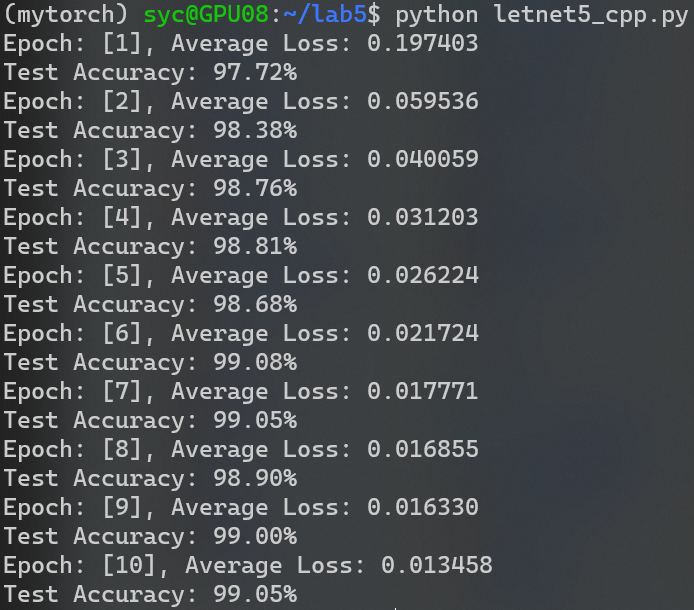
将自定义算子用于 LetNet-5 训练:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 from torch.utils.cpp_extension import load
gelu_cpp = load ( name = "gelu_cpp" , sources = [ "mygelu.cpp" ])
class my_gelu ( torch . autograd . Function ):
@staticmethod
def forward ( ctx , input ):
ctx . save_for_backward ( input )
output = gelu_cpp . forward ( input )
return output
@staticmethod
def backward ( ctx , grad_output ):
input , = ctx . saved_tensors
grad_input = gelu_cpp . backward ( grad_output , input )
return grad_input
class LeNet_5 ( nn . Module ):
...
def forward ( self , x ):
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . conv1 ( x ))
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . pool ( x ))
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . conv2 ( x ))
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . pool ( x ))
x = x . view ( - 1 , 16 * 4 * 4 )
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . full1 ( x ))
x = my_gelu . apply ( self . full2 ( x ))
x = self . full3 ( x )
return x
...
能够正常工作。
Reference
2024年3月18日
2023年10月22日
GoPoux4
GitHub